Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How does the medium affect the amplitude of free/natural vibrations of a body?
उत्तर १
The presence of the medium offers some resistance to motion, so the vibrating body continuously loses energy due to which the amplitude of the vibration continuously decreases.
उत्तर २
संबंधित प्रश्न
What are mechanical waves?
The adjacent diagram shows three different modes of vibrations P, Q and R of the same string.
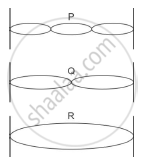
(i) Which vibration will produce a louder sound and why?
(ii) The sound of which string will have maximum shrillness?
(iii) State the ratio of wavelengths of P and R.
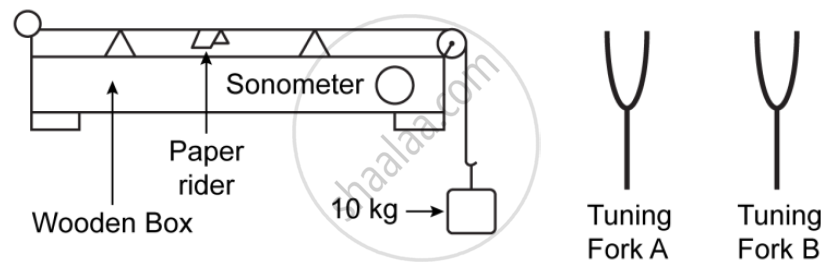
The diagram above shows a wire stretched over a sonometer. Stems of two vibrating tuning forks A and Bare touched to the wooden box of the sonometer. It is observed that the paper rider (a small piece of paper folded at the centre) present on the wire flies off when the stem of vibrating tuning fork B is touched to the wooden box but the paper just vibrates when the stem of vibrating tuning fork A is touched to the wooden box.
1) Name the phenomenon when the paper rider just vibrates.
2) Name the phenomenon when the paper rider flies off.
3) Why does the paper rider fly off when the stem of tuning fork B is touched to the box?
Why is a loud sound heard at resonance?
A vibrating tuning fork, held over an air column of a given length with its one end closed, produces a loud audible sound. Name the phenomenon responsible for it and explain the observation.
When a troop crosses a suspension bridge, the soldiers are asked to break steps. Explain the reason.
When a tuning fork, struck by a rubber pad, is held over a length of the air column in a tube, it produces a loud sound for a fixed length of the air column. Name the above phenomenon. How does the frequency of the loud sound compare with that of the tuning fork? State the unit for measuring loudness.
Explain Why are stringed musical instruments provided with large sound boxes?
Explain free and forced vibrations. Give an experimental arrangement to illustrate the phenomenon of resonance.
