Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Differentiate between the following:
Plasmolysis and Deplasmolysis.
उत्तर
| Plasmolysis | Deplasmolysis | ||
| 1. | In this, the protoplasm of the cell shrinks away from the cell wall. It results in the flaccid condition of the cells and the plant. | 1. | In this, the protoplasm of the cell swells up and touches the cell wall. It results in the turgid condition of the cells and the plant. |
| 2. | Caused due to exosmosis. | 2. | Caused by endosmosis. |
| 3. | It takes place when a plant cell is kept in a hypertonic solution. | 3. | It takes place when a plasmolysed celI is kept in a hypotonic solution. |
| 4. | It results in the flaccid condition of the plant. | 4. | It results in the turgid condition of the plant. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain Turgor pressure
Differentiate between the following:
Turgidity and Flaccidity
Give reason for the following:
It is better to transplant seedlings in a flower-bed in the evening and not in the morning.
Differentiate between:
Turgid and Flaccid.
Differentiate between the following
Turgor pressure and Root pressure
Give Technical Term for the following.
A cell in a fully extended condition.
Fill in the Blank
The condition opposite to turgid is ___________.
The hydrostatic pressure of the cell sap on the cell wall is called ______.
Give the equivalent term for the following:
Pressure exerted by the cell contents on the cell wall.
Given below is the figure of a plant cell showing different kinds of pressure acting upon it. Study the figure and answer the questions that follow:
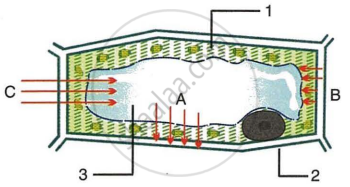
- In the figure, 1, 2 and 3 represent:
- Cytoplasm, Nucleus, Vacuole respectively
- Vacuole, Cytoplasm, Cell wall respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell membrane and vacuole respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell wall and Vacuole respectively.
- B in the figure represents:
- Osmotic pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Wall pressure
- Diffusion pressure
- A in the figure represents:
- irnbibition pressure
- Wall pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- C in the figure represents:
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- Wall pressure
- Imbibition pressure
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of a plasmolyzed plant cell.
