Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Fill in the Blank
The condition opposite to turgid is ___________.
उत्तर
The condition opposite to turgid is Flaccid.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The diagram below represents a process in plants. The setup was placed in bright sunlight. Answer the following questions:

a) Name the physiological process depicted in the diagram.
Why was oil added to the water?
b) When placed in bright sunlight for four hours, what do you observe with regard to the initial and final weight of the plant? Give a suitable reason for your answer
c) What happens to the level of water when this setup is placed in:
- Humid conditions?
- Windy conditions?
d) Mention any three adaptations found in plants to overcome the process mentioned in (i).
e) Explain the term ‘Guttation’.
Differentiate between the following:
Turgidity and Flaccidity
Mention whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F) and give an explanation in support of your answer.
Soaked seeds burst into three seed coats.
Differentiate between the following:
Plasmolysis and Deplasmolysis.
Give Technical Term for the following.
The pressure exerted by cell contents on a plant cell wall.
Multiple Choice Question:
When cell is fully turgid, which of the following will be zero?
Deplasmolysis occurs when a plasmolysed cell is placed in ______.
When the cells of a plant are fully distended, the condition is called ______.
The figure given below is a diagrammatic representation of a part of the cross-section of the root in the root hair zone. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
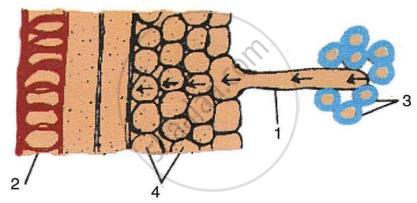
- The parts labelled as 1, 2, 3 and 4 are:
- Root hair, Xylem vessel, Soil particles, Cortex respectively.
- Xylem vessel, Soil particles, Root hair, Cortex respectively.
- Root hair, Xylem vessel, Cortex, Soil particles respectively.
- Cortex, Soil particles, Xylem vessel, Root hair respectively.
- The process that enables the passage of water from soil into the root hair is:
- Diffusion
- Active transport
- Osmosis
- Passive absorption
- The kind of force which exists between a liquid and any surface is called as:
- Cohesive force
- Adhesive force
- Capillarity
- Suction force
- The kind of force between the same kind of liquid molecules is:
- Capillary force
- Transpirational pull
- Adhesive force
- Cohesive force
- Sometimes exudation of water occurs from the margin of the leaves in the early morning or night. It is termed as:
- Transpiration
- Guttation
- Bleeding
- Osmosis
Given below is the figure of a plant cell showing different kinds of pressure acting upon it. Study the figure and answer the questions that follow:
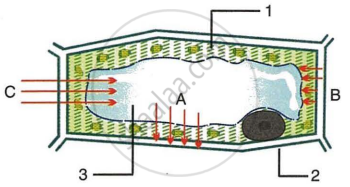
- In the figure, 1, 2 and 3 represent:
- Cytoplasm, Nucleus, Vacuole respectively
- Vacuole, Cytoplasm, Cell wall respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell membrane and vacuole respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell wall and Vacuole respectively.
- B in the figure represents:
- Osmotic pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Wall pressure
- Diffusion pressure
- A in the figure represents:
- irnbibition pressure
- Wall pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- C in the figure represents:
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- Wall pressure
- Imbibition pressure
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of a plasmolyzed plant cell.
