Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Distinguish between Conductors and Insulators.
उत्तर
Conductors and Insulators
| Conductors | Insulators | ||
| 1 | A substance which has very low electrical resistance is called a conductor. | 1 | A substance which has infinitely high electrical resistance is called an insulator. |
| 2 | Conductors contain charge carriers which can be easily accelerated by a potential difference. | 2 | Insulators do not contain charge carriers which can be easily accelerated by a potential difference. |
| 3 | Silver and copper are conductors. | 3 | Wood and glass are insulators. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a labelled diagram of Van de Graaff generator. State its working principle to show how by introducing a small charged sphere into a larger sphere, a large amount of charge can be transferred to the outer sphere. State the use of this machine and also point out its limitations.
The potential difference applied across a given resistor is altered so that the heat produced per second increases by a factor of 9. By what factor does the applied potential difference change?
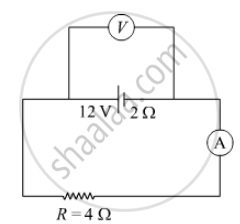
In the figure shown, an ammeter A and a resistor of 4 Ω are connected to the terminals of the source. The emf of the source is 12 V having an internal resistance of 2 Ω. Calculate the voltmeter and ammeter readings.
A metal rod of square cross-sectional area A having length l has current I flowing through it when a potential difference of V volt is applied across its ends (figure I). Now the rod is cut parallel to its length into two identical pieces and joined as shown in figure II. What potential difference must be maintained across the length of 2l. so that the current in the rod is still I?

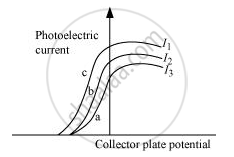
The figure shows a plot of three curves a, b, c, showing the variation of photocurrent vs collector plate potential for three different intensities I1, I2and I3 having frequencies v1, v2 and v3 respectively incident of a photosensitive surface.
Point out the two curves for which the incident radiations have same frequency but different intensities.
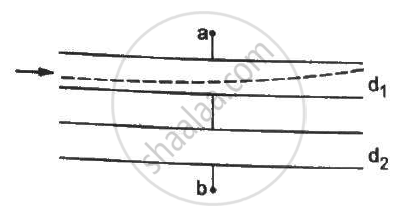
Both the capacitors shown in figure are made of square plates of edge a. The separations between the plates of the capacitors are d1 and d2 as shown in the figure. A potential difference V is applied between the points a and b. An electron is projected between the plates of the upper capacitor along the central line. With what minimum speed should the electron be projected so that it does not collide with any plate? Consider only the electric forces.
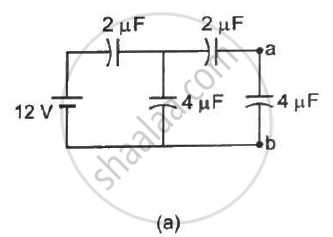
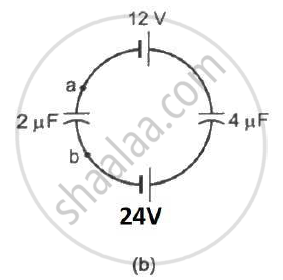
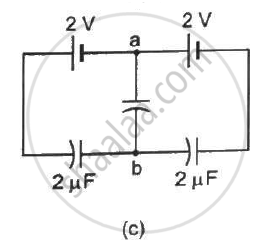
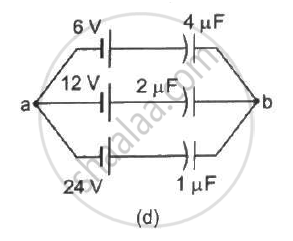
Find the potential difference `V_a - V_b` between the points a and b shown in each part of the figure.
A charge of `+2.0 xx 10^-8 C` is placed on the positive plate and a charge of `-1.0 xx 10^-8 C` on the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance `1.2 xx 10^-3 "uF"` . Calculate the potential difference developed between the plates.
A charge of 1 µC is given to one plate of a parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance 0⋅1 µF and a charge of 2 µC is given to the other plate. Find the potential difference developed between the plates.
The capacitance between the adjacent plates shown in figure is 50 nF. A charge of 1⋅0 µC is placed on the middle plate. (a) What will be the charge on the outer surface of the upper plate? (b) Find the potential difference developed between the upper and the middle plates.

A capacitor having a capacitance of 100 µF is charged to a potential difference of 50 V. (a) What is the magnitude of the charge on each plate? (b) The charging battery is disconnected and a dielectric of dielectric constant 2⋅5 is inserted. Calculate the new potential difference between the plates. (c) What charge would have produced this potential difference in absence of the dielectric slab. (d) Find the charge induced at a surface of the dielectric slab.
Answer the following question:
Find the expression for the resistivity of a material.
What will be the potential difference in the circuit when direct current is passed through the circuit?
The unit of potential difference as used in electrical circuits is ________.
Assertion: Electric potential and electric potential energy are different quantities.
Reason: For a system of positive test charge and point charge electric potential energy = electric potential.
On moving a charge of Q coulomb by X cm, W J of work is done, then the potential difference between the points is ______.
A bullet of mass of 2 g is having a charge of 2 µc. Through what potential difference must it be accelerated, starting from rest, to acquire a speed of 10 m/s.
Can there be a potential difference between two adjacent conductors carrying the same charge?
If potential difference between the two ends of a metallic wire is doubled, drift speed of free electrons in the wire ______.
