Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Distinguish between intracellular and extracellular digestion.
उत्तर
| Intracellular digestion | Extracellular digestion | |
| 1 | The digestion of food occurs within the cell. | The digestion occurs in the cavity of alimentary canal. |
| 2 | Digestive enzymes are secreted by the surrounding cytoplasm into the food vacuole. | Digestive enzymes are secreted by special cells into the cavity of alimentary canal. |
| 3 | Digestive products are diffused into the cytoplasm. | Digestive products diffuse across the intestinal wall into various parts of the body. |
| 4 | It is a less efficient method. | It is a more efficient method of digestion. |
| 5 | It occurs in unicellular organisms and some other lower organisms. | It occurs in multicellular organisms. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If you are given a specimen, what are the steps that you would follow to classify it?
What is the difference between direct and indirect development?
The following characteristics are essential for classification.
The largest division of the living world is ______.
Species is the ______ unit of classification.
Which of the following animals has a true coelom?
Which of the following have the highest number of species in nature?
Which of the following is a crustacean?
Match the following columns and select the correct option.
| Column – I | Column – II | ||
| (p) | Pila | (i) | Devil fish |
| (q) | Dentalium | (ii) | Chiton |
| (r) | Chaetopleura | (iii) | Apple snail |
| (s) | Octopus | (iv) | Tusk shell |
Observe the animal below and answer the following questions.

- Identify the animal.
- What type of symmetry does this animal exhibit?
- Is this animal Cephalized?
- How many germ layers does this animal have?
- How many openings does this animal’s digestive system have?
- Does this animal have neurons?
Choose the term that does not belong in the following group and explain why it does not belong?
Notochord, cephalisation, dorsal nerve cord and radial symmetry.
Examine the figures of diploblastic (i) and triploblastic (ii) organization in animals given below and identify the labelled parts A to D.
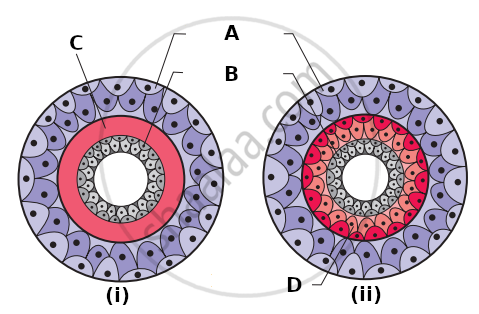
In some animal groups, the body is found divided into compartments with serial repitition of at least some organs. This characteristic feature is called ______.
Match the following list of animals with their level of organisation.
| Division of Labour | Animal |
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Organ level | i. Pheretima |
| B. Cellular aggregate level | ii. Fasciola |
| C. Tissue level | ii. Spongilla |
| D. Organ system level | iv. Obelia |
Choose the correct match showing division of labour with animal example.
Identify the phylum in which adults exhibit radial symmetry and larva exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Which group of chordates possess sucking and circular mouth without jaws?
Complete the paragraph using proper words:
(Asymmetrical, Paramecium, Equal, imaginary, central, insects, rats, bird, three, unequal)
If body of any animal is cut through ______ axis of body, it may or may not produce two equal halves. Depending upon this property, there are different types of animal bodies. In the case of ______ body, there is no any such imaginary axis of the body through which we can get two equal halves. For example Amoeba, ______ some sponges. In radial symmetry type of body, if imaginary cut passes through central axis but any plane of body, it gives two ______ halves. For example Starfish. In case of this animal, there are five different planes passing through ______ axis of body through which we can get two equal halves. In Bilateral symmetry type of body, there is only one such imaginary axis of body through which we can get two equal halves. For example: ______ fishes, frog, birds, human, etc.
