Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Distinguish between myopia and hypermetropia. Show diagrammatically how these defects can be corrected.
उत्तर
• Nearsightedness or Myopia − A person suffering from myopia can see only nearby objects clearly, but cannot see the objects beyond a certain distance clearly.
Myopic eye: 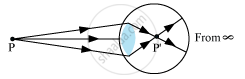
Correction − In order to correct the eye for this defect, a concave lens of suitable focal length is placed close to the eye so that the parallel ray of light from an object at infinity after refraction through the lens appears to come from the far point P'of the myopic eye.
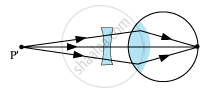
• Farsightedness or Hypermetropia − A person suffering from hypermetropia can see distant objects clearly, but cannot see nearby objects.
Hypermetropic eye:
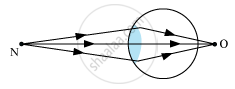
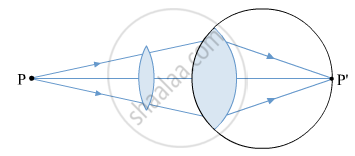
Correction − To correct this defect, a convex lens of suitable focal length is placed close to the eye so that the rays of light from an object placed at the point N after refraction through the lens appear to come from the near point N'of the hypermetropic eye.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Magnifying power of a simple microscope is inversely proportional to the focal length of the lens. What then stops us from using a convex lens of smaller and smaller focal length and achieving greater and greater magnifying power?
Draw a ray diagram showing image formation in a compound microscope ?
How is 'limit of resolution' related to resolving power of a microscope ?
An object is to be seen through a simple microscope of focal length 12 cm. Where should the object be placed so as to produce maximum angular magnification? The least distance for clear vision is 25 cm.
Consider the following two statements :-
(A) Line spectra contain information about atoms.
(B) Band spectra contain information about molecules.
Draw a neat labelled ray diagram showing the formation of an image at the least distance of distinct vision D by a simple microscope. When the final image is at D, derive an expression for its magnifying power at D.
compound microscope consists of two convex lenses of focal length 2 cm and 5 cm. When an object is kept at a distance of 2.1 cm from the objective, a virtual and magnified image is fonned 25 cm from the eye piece. Calculate the magnifying power of the microscope.
Define the magnifying power of a microscope in terms of visual angle.
A convex lens of a focal length 5 cm is used as a simple microscope. Where should an object be placed so that the image formed by it lies at the least distance of distinct vision (D = 25 cm)?
The near vision of an average person is 25 cm. To view an object with an angular magnification of 10, what should be the power of the microscope?
