Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a diagram to show the standing pressure wave and standing displacement wave for the 3rd overtone mode of vibration of an open organ pipe.
उत्तर
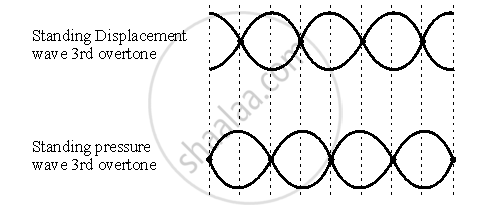
The displacement node is a pressure anti-node and via-versa.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The transverse displacement of a string (clamped at its both ends) is given by
y(x, t) = 0.06 sin `2/3` x cos (120 πt)
where x and y are in m and t in s. The length of the string is 1.5 m and its mass is `3.0 xx 10^(-2)` kg.
Answer the following :
Determine the tension in the string.
A travelling harmonic wave on a string is described by
`y(x,t) = 7.5 sin (0.0050x + 12t + pi/4)`
(a) What are the displacement and velocity of oscillation of a point at x = 1 cm, and t =1 s? Is this velocity equal to the velocity of wave propagation?
(b) Locate the points of the string which have the same transverse displacements and velocity as the x = 1 cm point at t = 2 s, 5 s and 11 s.
One end of a long string of linear mass density 8.0 × 10–3 kg m–1 is connected to an electrically driven tuning fork of frequency 256 Hz. The other end passes over a pulley and is tied to a pan containing a mass of 90 kg. The pulley end absorbs all the incoming energy so that reflected waves at this end have negligible amplitude. At t = 0, the left end (fork end) of the string x = 0 has zero transverse displacement (y = 0) and is moving along positive y-direction. The amplitude of the wave is 5.0 cm. Write down the transverse displacement y as the function of x and t that describes the wave on the string.
The transverse displacement of a string (clamped at its both ends) is given by
y(x, t) = 0.06 sin `2/3` x cos (120 πt)
where x and y are in m and t in s. The length of the string is 1.5 m and its mass is 3.0 × 10-2 kg.
Answer the following:
Interpret the wave as a superposition of two waves travelling in opposite
directions. What is the wavelength, frequency, and speed of each wave?
A transverse harmonic wave of amplitude 0.01 m is generated at one end of a long horizontal string by a tuning fork of frequency 500 Hz. At a given instant of time, the displacement of a particle at a distance of 0.2 m from the fork is – 0.005 m and that of a particle at a distance of 0.1 m is + 0.005 m. The wavelength is
The equation of a simple harmonic progressive wave is given by y = A sin (100πt − 3x). Find the distance between 2 particles having a phase difference of `π/3`.
The earth has a radius of 6400 km. The inner core of 1000 km radius is solid. Outside it, there is a region from 1000 km to a radius of 3500 km which is in molten state. Then again from 3500 km to 6400 km the earth is solid. Only longitudinal (P) waves can travel inside a liquid. Assume that the P wave has a speed of 8 km s–1 in solid parts and of 5 km s–1 in liquid parts of the earth. An earthquake occurs at some place close to the surface of the earth. Calculate the time after which it will be recorded in a seismometer at a diametrically opposite point on the earth if wave travels along diameter?
In the given progressive wave y = 5 sin (100 πt – 0.4 πx) where y and x are in m, t is in s. What is the amplitude.
In the given progressive wave y = 5 sin (100 πt – 0.4 πx) where y and x are in m, t is in s. What is the wavelength.
In the given progressive wave y = 5 sin (100 πt – 0.4 πx) where y and x are in m, t is in s. What is the frequency.
In the given progressive wave y = 5 sin (100 πt – 0.4 πx) where y and x are in m, t is in s. What is the wave velocity.
In the given progressive wave y = 5 sin (100 πt – 0.4 πx) where y and x are in m, t is in s. What is the particle velocity amplitude..
