Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw the structure of the pyran.
उत्तर
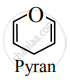
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the action of the following reagents on glucose?
acetic anhydride
Define carbohydrates.
Draw the Haworth projection structure of the following.
α-D-(–)-Fructofuranose
Identify the bond that links the carbon of two adjacent monosaccharides.
Identify the given structure 'P' and 'Q'.
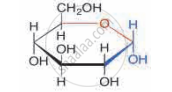
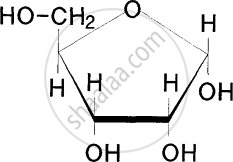
From the following identify the materials that are made up of cellulose.
i. Plant cell wall
ii. Exoskeleton of arthropods
iii. Paper from plant pulp
iv. Cotton fibre
____________ do not give smaller sugar units on hydrolysis.
Monosaccharides are ______ in nature.
From the following identify the two types of glucose polymers present in starch.
Match the columns and select the correct option.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| i. | Starch | a. | Animal storage molecule |
| ii. | Cellulose | b. | Plant storage molecule |
| iii. | Glycogen | c. | Heparin |
| iv. | Heteropolysaccharide | d. | Plant cell wall component |
All these carbohydrates contain \[\ce{1 -> 4β}\] glycosidic linkage, EXCEPT ____________.
Identify the INCORRECT statement regarding glucose.
Which one of the following is an oligosaccharide?
Which one of the following carbohydrates is insoluble in water?
What is the molecular formula of glyceraldehyde?
How many optical isomers are possible for a compound having four asymmetric carbon atoms?
The number of sp2 and sp3 hybridised carbon in fructose are respectively ____________.
Glucose is an aldose. Which one of the following reactions is not expected with glucose?
Glucose on oxidation with bromine water yields gluconic acid. This reaction confirms the presence of ______.
Match the Column I with Column II and choose the correct answer from options below:
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Purine | 1. Glycogen |
| B. Pyrimidine | 2. Cellulose |
| C. Structural polysaccharide | 3. Glucagon |
| D. Storage polysaccharide | 4. Adenine |
| 5. Cytosine |
Describe the action of the following reagent on glucose:
Bromine water
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
Why are carbohydrates generally optically active?
\[\ce{CH2OH-CO-(CHOH)4-CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
\[\ce{CH2OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
\[\ce{CH2OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
