Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw the structure of the pyran.
Solution
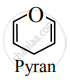
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give scientific reasons:
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called inversion.
The glycosidic linkage in maltose is formed between _______________
Write the name of the polysaccharide used for the commercial preparation of glucose.
What is the action of the following reagents on glucose?
hydrogen iodide
Draw the Haworth projection structure of the following.
α-D-(–)-Fructofuranose
What is monosaccharide?
Identify the given structure 'P' and 'Q'.
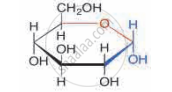
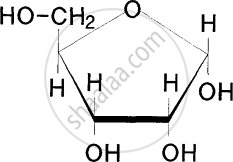
From the following identify an example of disaccharides.
Carbohydrates can contain which of the following chemical groups?
From the following identify the materials that are made up of cellulose.
i. Plant cell wall
ii. Exoskeleton of arthropods
iii. Paper from plant pulp
iv. Cotton fibre
By which of the following feature we can identify the relatively small DNA molecules of plasmids?
Identify a non-reducing carbohydrate from the following.
Identify the CORRECT combination.
4-O-(α-D-Glucopyranosyl)-D-glucopyranose is ____________.
Which among the following sugars does not reduce Tollen's reagent?
When one mole of lactose is hydrolysed, the hydrolysate contains ____________.
Which of the following are epimers?
Lactose is made of ______.
Formation of gluconic acid from glucose by oxidation using Br2 water.
The glycosidic linkage present in maltose is ______.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
Assign D/L configuration to the following monosaccharides:
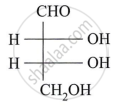
Carbohydrates that do not undergo hydrolysis further are called ______.
CH2 OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2 OH is an example of ______.
Why are carbohydrates generally optically active?
Write the Zwitter ion structure of alanine.
\[\ce{CH2OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
\[\ce{CH2OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
