Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
During refrigeration cycle, heat is rejected by the refrigerant in the ______.
विकल्प
Condenser
Cold chamber
Evaporator
Hot chamber
उत्तर
During refrigeration cycle, heat is rejected by the refrigerant in the condenser.
Explanation:
In the condenser, the heat is rejected by the refrigerant into the atmosphere, and then the refrigerant goes to the expansion valve. The condenser is made up of copper or aluminium coils since their conductivity is high to ensure the better transfer of heat from a hot region to the atmosphere. The condenser sometimes also contains some additional length to subcool the liquid below the saturation temperature.
संबंधित प्रश्न
A refrigerator is to maintain eatables kept inside at 9°C. If the room temperature is 36° C, calculate the coefficient of performance.
If α is the coefficient of performance of a refrigerator and 'Q1' is heat released to the hot reservoir, then the heat extracted from the cold reservoir 'Q2' is ______.
A refrigerator works between 4°C and 30°C. It is required to remove 600 calories of heat every second in order to keep the temperature of the refrigerated space constant. The power required is (Take 1 cal = 4.2 joules).
Consider a heat engine as shown in figure Q1 and Q2 are heat added to heat bath T1 and heat taken from T2 in one cycle of engine. W is the mechanical work done on the engine. If W > 0, then possibilities are ______.
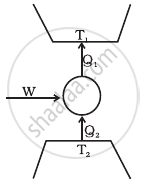
- Q1 > Q2 > 0
- Q2 > Q1 > 0
- Q2 < Q1 < 0
- Q1 < 0, Q2 > 0
If a refrigerator’s door is kept open, will the room become cool or hot? Explain.
If the co-efficient of performance of a refrigerator is 5 and operates at the room temperature (27°C), find the temperature inside the refrigerator.
What are the steps through which a refrigerant goes in one complete cycle of refrigeration?
Explain the mechanism of a refrigerator with the help of a schematic diagram.
The coefficient of performance of a room air conditioner is 3. If the rate of doing work is 2 kW, the heat current is ______.
