Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Elucidate the formation of n-type extrinsic semiconductors.
उत्तर
N-type semiconductor: A n-type semiconductor is obtained by doping a pure Germanium (or Silicon) crystal with a dopant from group V pentavalent elements like Phosphorus, Arsenic, and Antimony. The dopant has five valence electrons while the Germanium atom has four valence electrons.
During the process of doping, a few of the Germanium atoms are replaced by the group V dopants. Four of the five valence electrons of the impurity atom are bound with the 4 valence electrons of the neighbouring replaced Germanium atom. The fifth valence electron of the impurity atom will be loosely attached to the nucleus as it has not formed the covalent bond.
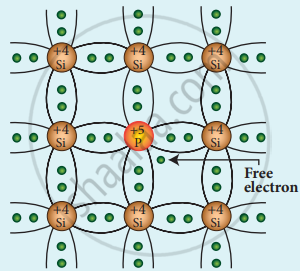
Free electron which is loosely attached to the lattice
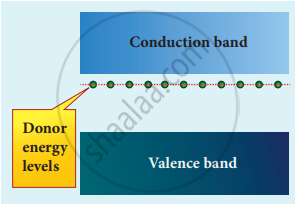
Representation of donor energy level
The energy level of the loosely attached fifth electron from the dopant is found just below the conduction band edge and is called the donor energy level. At room temperature, these electrons can easily move to the conduction band with the absorption of thermal energy. It is shown in the figure. Besides, an external electric field also can set free the loosely bound electrons and lead to conduction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Doping a semiconductor result in
Why is temperature co-efficient of resistance negative for semiconductor?
What do you mean by doping?
Distinguish between intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors.
Why can’t we interchange the emitter and collector even though they are made up of the same type of semiconductor material?
On doping an intrinsic semiconductor with a group V element, free electrons in the conduction band are the majority charge carriers and the resulting semiconductor has a net
The electron concentration in an n-type semiconductor is the same as the hole concentration in a p-type semiconductor. An external field (electric) is applied across each of them. Compare the currents in them.
The electron concentration in an n-type semiconductor is the same as the hole concentration in a p-type semiconductor. An external field (electric) is applied across each of them. Compare the currents in them.
The electron concentration in an n-type semiconductor is the same as the hole concentration in a p-type semiconductor. An external field (electric) is applied across each of them. Compare the currents in them.
