Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain how the following metals are obtained from their compounds by the reduction process:
(i) Metal M which is in the middle of the reactivity series.
(ii) Metal N which is high up in the reactivity series.
Give one example of each type
उत्तर
(i) Metals that are present at the centre of the reactivity series are moderately-reactive. Therefore, metal M is a moderately-reactive metal. After obtaining the metal oxides from ores, the metal oxides are reduced to obtain the pure metals. As metal M is a moderately reactive metal, its oxide can be reduced by using coke (carbon).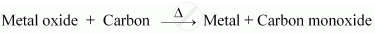
One example of metal M: Iron (Fe)
(ii) Metals that are present higher up in the reactivity series are very reactive metals. Hence, metal N is a highly reactive metal. Oxides of highly reactive metals cannot be reduced by using coke. Therefore, these metals are reduced by passing electric current throughtheir molten salts. This process is known as electrolytic reduction.
One example of metal N: Sodium (Na)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name one method for the refining of metals.
What is meant by refining of a metal? Name the most widely used method for the refining of impure metals obtained by various reduction processes. Describe this method with the help of a labelled diagram by taking the example of any metal.
Name any five metals which are purified by electrolytic refining method.
Draw a neat labelled diagram.
Froth floatation method.
The lightest liquid metal is ____________.
\[\ce{Cu2S + 3Cu2O -> 6Cu + SO2}\]
The above process is:
Reaction between X and Y, forms compound Z. X loses electron and Y gains electron. Which of the following properties is not shown by Z?
What are the constituents of solder alloy? Which property of solder makes it suitable for welding electrical wires?
Answer the following question with reference to the electrorefining of copper:
What do you observe at the cathode?
Answer the following questions with reference to the electrorefining of copper:
Write the reaction taking place at the cathode.
