Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the mechanism of sex determination in birds.
उत्तर
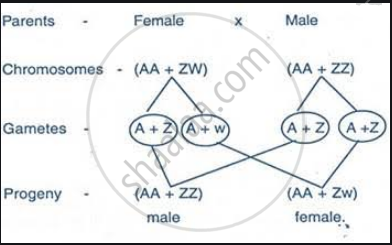
The sex chromosomes in birds are designated Z and W, and the male is the homomorphic sex (ZZ) and the female heteromorphic (ZW). In most avian species the Z chromosome is a large chromosome, usually the fourth or fifth largest, and it contains almost all the known sex-linked genes. The W chromosome is generally a much smaller microchromosome, containing a high proportion of repeat sequence DNA. Recently a gene encoding a protein involved in transcriptional activation of chromatin has been detected on the W chromosome. The weight of evidence suggests that sex determination in birds is by a genic balance mechanism, in which the ratio of autosomes to Z chromosomes is the crucial factor. DNA sequences homologous to the testis determining factor in humans have been detected in both male and female birds, but it is not clear that they have a sex-related function in birds. A number of different practical methods have been developed to distinguish the sex of birds, based on sex-linked genes, the amount of DNA per cell and using DNA probes for sex-linked sequences.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Differentiate between male and female heterogamety
Write notes on sex determination in the unborn baby.
Which of the following is an example of ZW – ZZ type of mechanism of sex determination?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Genes always work in ................ .
E is the gene for brown eye colour and an is the gene for blue eye colour. which gene is (1) recessive, and (2) dominant?
The person A has only B chromosomes in all its gametes. On the other hand, another person C has chromosome D in half of gametes and chromosome E in the other half of gametes. When chromosomes B and D combine during fertilisation, a female zygote results. On the other hand, combination of B and E chromosomes produces a male zygote.
(a) What are chromosomes (i) B (ii) D, and (iii) E?
(b) Out of B, D and E, which two chromosomes are of the same type?
(c) Which chromosome is smaller in size?
(d) What is the general name of chromosomes such as B and E?
(e) Out of the two persons A and C, which one is (i) male, and (ii) female?
Name two animals which have nineteen pairs of chromosomes.
In which livings, female decides the sex? Give two examples.
Write the functional activity of the following structure:
Heterosomes
How drones are produced in honey bees?
XO type of sex determination and XY type of sex determination are examples of ____________.
ZW-ZZ system of sex determination occurs in
There are five daughters and no son in a family. It is because
Match the items of Column I with Column II:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| i. | XX-XO method of Sex Determination | a. | Turner syndrome |
| ii. | XX-XY method of Sex Determination | b. | Female heterog ametic |
| iii. | karyotype-45 | c. | Grasshopper |
| iv. | ZW-ZZ method of Sex Determination | d. | Female homogametic |
Which of the following determines the sex of a child?
Some dinosaurs had feathers although they could not fly but birds have feathers that help them to fly. In the context of evolution this means that
A woman has only daughters. Analyse the situation genetically and provide a suitable explanation.
The belief that the mother is completely responsible for the sex of the child is wrong because the child
All human chromosomes ate not paired. Most human chromosomes have a maternal and a paternal copy, and we have 22 such pairs. But one pair called the sex chromosomes, is odd in not always being a perfect pair. Women have a perfect pair of sex chromosomes. But men have a mismatched pair in which one is normal sized while the other is a short one.
(a) In humans, how many chromosomes are present in a Zygote and in each gamete?
(b) A few reptiles rely entirely on environmental cues for sex determination. Comment.
(c) "The sex of a child is a matter of chance and none of the parents are considered to be responsible for it." Justify it through flow chart only.
OR
(c) Why do all the gametes formed in human females have an X chromosome?
