Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the mechanism of sex determination in birds.
Solution
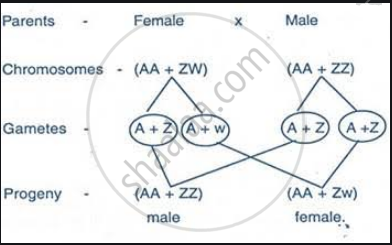
The sex chromosomes in birds are designated Z and W, and the male is the homomorphic sex (ZZ) and the female heteromorphic (ZW). In most avian species the Z chromosome is a large chromosome, usually the fourth or fifth largest, and it contains almost all the known sex-linked genes. The W chromosome is generally a much smaller microchromosome, containing a high proportion of repeat sequence DNA. Recently a gene encoding a protein involved in transcriptional activation of chromatin has been detected on the W chromosome. The weight of evidence suggests that sex determination in birds is by a genic balance mechanism, in which the ratio of autosomes to Z chromosomes is the crucial factor. DNA sequences homologous to the testis determining factor in humans have been detected in both male and female birds, but it is not clear that they have a sex-related function in birds. A number of different practical methods have been developed to distinguish the sex of birds, based on sex-linked genes, the amount of DNA per cell and using DNA probes for sex-linked sequences.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How is the sex of the child determined in human beings?
What are the chromosomes XY and XX known as?
The exchange of genetic material takes place in :
(a) vegetative reproduction
(b) asexual reproduction
(c) sexual reproduction
(d) budding
Both father and mother have the genes Ee in their cells. What colour are their eyes?
Which combination of genes in the zygote will produce children with brown eyes?
The person A has only B chromosomes in all its gametes. On the other hand, another person C has chromosome D in half of gametes and chromosome E in the other half of gametes. When chromosomes B and D combine during fertilisation, a female zygote results. On the other hand, combination of B and E chromosomes produces a male zygote.
(a) What are chromosomes (i) B (ii) D, and (iii) E?
(b) Out of B, D and E, which two chromosomes are of the same type?
(c) Which chromosome is smaller in size?
(d) What is the general name of chromosomes such as B and E?
(e) Out of the two persons A and C, which one is (i) male, and (ii) female?
Choose the correct answer:
A man can transfer his sex-linked gene to his ______________
Answer the following question:
How is sex determined in human beings? Explain with the help of a diagram.
Explain the haplo-diploid method of sex determination in the honey bee.
From the following which option correctly represents the normal genetic constitution of a ovum?
Which of the following develops through parthenogene is?
Grasshopper is an example of XO type of sex determination in which the males have ______.
In XO type of sex determination ______.
In human males all the chromosomes are paired perfectly except one. This/these unpaired chromosomes is/are ______.
- large chromosome
- small chromosome
- Y-chromosome
- X-chromosome
Which of the following is an example of genetic variation?
Sex in honey bee is determined by ______.
In humans, males are heterogametic and females are homogametic. Explain. Are there any examples where males are homogametic and females heterogametic?
Does a male child inherit X chromosome from his father? Justify.
What is the probability of a girl or a boy being born into a family? Justify your answer.
