Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the process of transcription in Eukaryotes.
उत्तर
Transcription is the process of formation of RNA molecules from DNA. During transcription, only a segment of DNA from only one of the strands participates. The strand with 3' → 5' polarity acts as a template for RNA and is called template strand. The complementary DNA strand is called a coding strand, which is a misnomer.
Transcription takes place in following three steps:
(1) Initiation
-
RNA polymerase binds with the promoter sequence to initiate the process of transcription.
- Association with initiation factors alters the specificity of RNA polymerase to initiate the transcription.

(2) Elongation
- RNA polymerase uses nucleoside triphosphate as substrate, and polymerisation occurs according to complementarity.
- Sigma subunit dissociates as the RNA polymerase enters elongation phase.
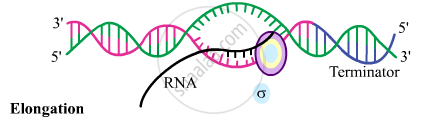
(3) Termination
-
Termination occurs when termination factor (rho protein) alters the specificity of RNA polymerase to terminate the transcription.
As the RNA polymerase proceeds to perform elongation, a short stretch of RNA remains bound to the enzyme. As the enzyme reaches the termination region, this nascent RNA falls off and transcription is terminated.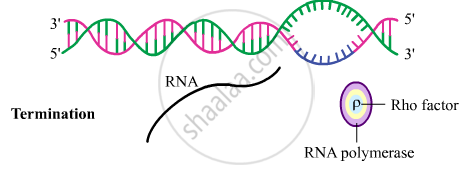
The precursor of mRNA, i.e. hnRNA, undergoes many changes before proceeding to translation. Since it contains both coding (exons) and non-coding regions (introns), it also undergoes splicing. These changes are collectively known as post-transcriptional modifications. These are as follows:
- Capping - In this, 7-methyl guanosine triphosphate is added to the 5' end of hnRNA.
-
Tailing - In this, adenylate residues are added to the 3' end of hnRNA by the enzyme poly (A) synthetase.
- Splicing - The hnRNA contains both introns and exons. Introns are removed and exons are joined by a process called splicing.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Construct and label a transcription unit from which the RNA segment given below has been transcribed. Write the complete name of the enzyme that transcribed this RNA.

Methyl guanosine triphosphate is added at 5' end of hn-RNA in a process of ______.
To initiate translation, the mRNA first binds to ______.
In transcription in eukaryotes, heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA) is transcribed by ______.
On the ribosome, mRNA binds ______ and two sites in the ______ for subsequent amino acids to bind to be close enough to each other for the formation of a peptide bond.
A special feature of viruses is that they:
The most likely method, used to determine the structural details of the cell organelle is ______.
Which of the following pair lack the unit membrane?
Which is the “Only enzyme” that has “Capability” to catalyse Initiation, Elongation and Termination in the process of transcription in prokaryotes?
Observe the segment of mRNA given below.

(a) Explain and illustrate the steps involved to make fully processed hnRNA?
(b) Gene encoding RNA Polymerase I and III have been affected by mutation in a cell. Explain its impact on the synthesis of a polypeptide, stating the reasons.
