Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the construction and working of an electric generator (AC) with the help of a neat diagram.
उत्तर
A generator which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in the form of alternating current is called A.C. generator.
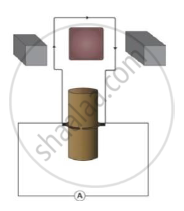
Construction: The main components of A.C. generator are:
- Rectangular coil: A large number of turns of insulated copper wire wound on iron core in rectangular shape form a coil ABCD as shown in the figure.
- Strong magnets: The coil is placed in between two pole pieces (N and S) of a strong magnet. This provides a strong magnetic field.
- Rings: The two ends of the coil are connected to two rings R1 and R2. These rings rotate along with the coil.
- Brushes: Two carbon brushes B1 and B2 are used to press the rings.
- Axle: The two rings have resistive coating in their inner surfaces and are tightly fitted on the axle and the function of the axle is to rotate with the coil.

Working:
- When the axle is rotated with the help of a machine from outside, the coil ABCD starts rotating.
- On rotating the axle, the branch AB move upwards and branch CD move downwards hence coil ABCD rotates clockwise.
- According to Fleming’s right-hand rule, electric current flows in the direction A→B→C→D. Therefore, current flows from B2 to B1 in the external circuit through a galvanometer.
- After half rotation, the branch AB and CD exchange their position and the induced current flows as D→B→A.
- Since, branch BA is in contact with brush B1 and branch DC is in contact with B2, current flow from B1 to B2 in the external circuit i.e., in the direction opposite to the previous half rotation.
- This repeats after every half rotation and in this way, an alternate current is produced using an AC generator.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name some sources of direct current.
A rectangular coil of copper wires is rotated in a magnetic field. The direction of the induced current changes once in each______.
A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is pushed into the coil?
What change should be made in an a.c. generator so that it may become a d.c. generator?
What is the major difference between the simple alternator and most practical alternators?
Complete the following sentence:
A generator with commutator produces ............... current.
An electric generator converts:
(a) electrical energy into mechanical energy.
(b) mechanical energy into heat energy.
(c) electrical energy into chemical energy.
(d) mechanical energy into electrical energy.
The frequency of alternating current (a.c.) supply in India is:
(a) 0 Hz
(b) 50 Hz
(c) 60 Hz
(d) 100 Hz
The current induced in a closed circuit only if there is ______.
What determines the frequency of a.c. produced in a generator?
Draw a labelled diagram of a simple a.c. generator.
What energy conversion does take place in a generator when it is in use?
Explain the construction and working of the following. Draw a neat diagram and label it.
Electric Generator (AC)
Explain the difference:
AC generator and DC generator.
Observe the figure and answer the following questions.
a) Identify the machine shown in figure.
b) Write a use of this machine.
c) How transformation of energy takes place in this machine.
An a.c. generator changes the ______energy to ______ energy.
A flat coil of wire rotates at a constant speed about an axis perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field. Draw a graph to show how the induced e.m.f. varies relative to the positions of the coil during its one complete rotation. At what position of the coil, the e.m.f. has the maximum value?
A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer forming a loop and a magnet is:
A: Held stationary
B: Moved away along its axis
C: Moved towards along its axis
D: There will be an induced current in
State one factor that affects the magnitude of induced current in an AC generator.
