Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the construction and working of an electric generator (AC) with the help of a neat diagram.
Solution
A generator which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in the form of alternating current is called A.C. generator.
Construction: The main components of A.C. generator are:
- Rectangular coil: A large number of turns of insulated copper wire wound on iron core in rectangular shape form a coil ABCD as shown in the figure.
- Strong magnets: The coil is placed in between two pole pieces (N and S) of a strong magnet. This provides a strong magnetic field.
- Rings: The two ends of the coil are connected to two rings R1 and R2. These rings rotate along with the coil.
- Brushes: Two carbon brushes B1 and B2 are used to press the rings.
- Axle: The two rings have resistive coating in their inner surfaces and are tightly fitted on the axle and the function of the axle is to rotate with the coil.

Working:
- When the axle is rotated with the help of a machine from outside, the coil ABCD starts rotating.
- On rotating the axle, the branch AB move upwards and branch CD move downwards hence coil ABCD rotates clockwise.
- According to Fleming’s right-hand rule, electric current flows in the direction A→B→C→D. Therefore, current flows from B2 to B1 in the external circuit through a galvanometer.
- After half rotation, the branch AB and CD exchange their position and the induced current flows as D→B→A.
- Since, branch BA is in contact with brush B1 and branch DC is in contact with B2, current flow from B1 to B2 in the external circuit i.e., in the direction opposite to the previous half rotation.
- This repeats after every half rotation and in this way, an alternate current is produced using an AC generator.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The essential difference between an AC generator and a DC generator is that
State whether the following statement is true or false.
An electric motor converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
What type of generator is used at Power Stations?
What change should be made in an a.c. generator so that it may become a d.c. generator?
What is the major difference between the simple alternator and most practical alternators?
Complete the following sentence:
A generator with commutator produces ............... current.
Draw the labelled diagram of an A.C. generator. With the help of this diagram, explain the construction and working of an A.C. generator.
Name and state the principle of a simple a.c. generator. What is its use?
Draw a labelled diagram of a simple a.c. generator.
Suggest two ways in an a.c. generator to produce a higher e.m.f.
State one advantage of using a.c. over d.c.
A flat coil of wire rotates at a constant speed about an axis perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field. Draw a graph to show how the induced e.m.f. varies relative to the positions of the coil during its one complete rotation. At what position of the coil, the e.m.f. has the maximum value?
The given figures 1 to 3 show the working of a simple A.C. generator. Study the diagrams and answers of the following questions.
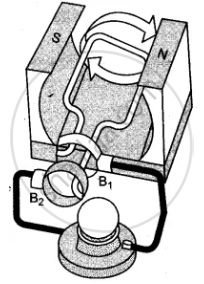
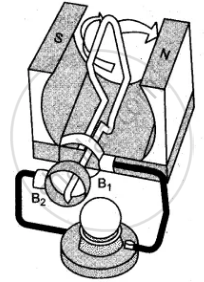
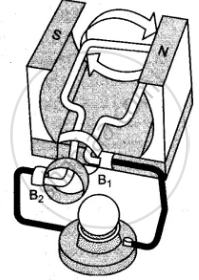
(i) State and explain the principle underlying the working of a simple generator.
(ii) Where is the loop of wire placed?
(iii) What happens when the loop is rotated?
(iv) Indicate the direction of the current flow through the wire for the first half of the turn (in first figure). Name and state the rule used in finding the direction of the current.
(v) Indicate the direction of the current for the case shown in second figure.
(vi) Indicate the direction of current in the outer circuit (i.e., electric bulb) in first and third figure.
(vii) What type of current is shown in the above diagrams? Explain.
State true or false:
The frequency of AC is 50 Hz.
A device for producing electric current is ______.
A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is withdrawn from inside the coil?
An AC generator is provided with ______ slip rings that rotate with the coil.
State one factor that affects the magnitude of induced current in an AC generator.
