Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the glycolysis in detail.
उत्तर
Glycolysis was first described by Embden, Meyerhof, and Parnas, and it is commonly referred to as the EMP pathway. This process occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is found in all living organisms.
In glycolysis, a molecule of glucose (6-carbon) undergoes partial oxidation to form two molecules of pyruvic acid (3-carbon each). This process is energy-yielding, producing a net gain of 2 ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules.
The pyruvic acid formed can:
- Enter the Krebs cycle (aerobic respiration) if oxygen is present, where further energy is extracted.
- Undergo fermentation (anaerobic respiration) if oxygen is absent, resulting in the formation of lactate or ethanol, depending on the organism.
The steps involved in the partial oxidation of glucose to form pyruvate are as follows:
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Given below are the end products of different reactions involving glucose. Write the appropriate end product in front of the following:
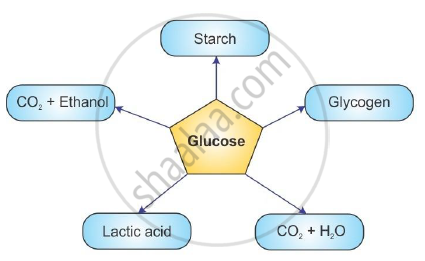
(1) Anaerobic reaction =
(2) Reaction in human muscles =
(3) Aerobic respiration
(4) Reaction in plant cells =
(5) Reaction in liver =
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans
Which is the basic requirement of living organisms for obtaining energy?
Which of the following type of energy is used by living organisms to perform vital life processes? Kinetic energy, Chemical energy, Potential energy, Nuclear energy
Match the organisms given in column I with the processes given in column II:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Leech | (a) | Holozoic nutrition |
| (ii) | Amoeba | (b) | Autotrophic nutrition |
| (iii) | Mushroom | (c) | Parasitic nutrition |
| (iv) | Green plant | (d) | Saprophytic nutrition |
Match the terms in column I with those in column II :
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Trypsin | (a) | Liver |
| (ii) | Amylase | (b) | Gastric glands |
| (iii) | Bile | (c) | Pancreas |
| (iv) | Pepsin | (d) | Saliva |
A person lives near a forest. Make a list of four items which he can get from the forest to meet his daily needs.
Name the green dot like structures in some cells observed by a student when a leaf peel was viewed under a microscope. What is this green colour due to?
Skin : Keratin : : Blood : ____________
Rewrite the food-chain given below with correct sequence.
Grasshopper– Snake– Paddyfield– Eagle– Frog
Complete the following flowchart.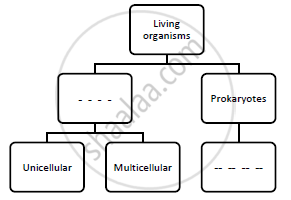
Fill in the blank and explain the statement.
Our muscle cells perform ______ type of respiration during exercise.
Write definition.
Nutrition.
Write definition
Nutrients
Write the definition.
Proteins
Distinguish between Glycolysis and TCA cycle.
Give scientific reason.
Oxygen is necessary for complete oxidation of glucose.
Give scientific reason.
Kreb's cycle is also known as citric acid cycle.
Write the forms to which following food materials are converted after digestion.
1.Milk
2. Potato.
3. Oil.
4. Chapati
Complete the following chart and state which process of energy production it represents:

Why is there a difference in the rate of breathing between aquatic organisms and terrestrial organisms? Explain.
Name the organs that form the excretory system in human beings.
Find an odd one out.
Explain the Steps of Glycolysis.
Choose the forms in which most plants absorb nitrogen
- Proteins
- Nitrates and Nitrites
- Urea
- Atmospheric nitrogen
How do the guard cells regulate opening and closing of stomatal pores?
In each of the following situations what happens to the rate of photosynthesis?
- Cloudy days
- No rainfall in the area
- Good manuring in the area
- Stomata get blocked due to dust
Classify vitamins according to their solubility.
Give one example of each of the classifications of vitamins.
