Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the Ratio or percentage method of measuring price elasticity of demand.
उत्तर
Ratio method is developed by Prof. Marshall. According to this method, elasticity of demand is measured by dividing the percentage change in demand by the percentage change in price. Percentage method is also known as Arithmetic method. Price elasticity is measured as :
Elasticity of Demand (Ed) = `"Percentage change in Quantity demanded"/"Percentage change in Price"`
Ed = `(%Delta"Q")/(%Delta"P")`
Mathematically, the above formula can be presented as under.
Ed = `((Delta"Q")/"Q")/((Delta"P")/"P")`
∴ Ed = `(Delta"Q")/"Q"xx"P"/(Delta"P")`
Q = Original quantity demanded
ΔQ = Difference between the new quantity and original quantity demanded.
P = Original price
ΔP = Difference between new price and original price
For example:
Calculate the Price Elasticity of Demand if the demand for Good X increases from 5 units to 7 units due to fall in price from Rs. 10 to Rs. 6.
Elasticity of Demand (Ed) = `"Percentage change in Quantity demanded"/"Percentage change in Price"`
Percentage change in Quantity demanded = `("change in Quantity"(Delta"Q"))/("Initial quantity"("Q"))xx100`
= `(7-5)/5xx100`
= 40%
Percentage change in price = `("Change in Price"(Delta"P"))/("Original Price" ("P"))xx100`
= `(6-10)/10xx100`
= -40%
= `-40%/40%`
= -1 or 1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The price elasticity of demand on a linear demand curve at the X-axis is ______.
Complete the correlation:
Straight-line demand curve : Linear demand curve :: _______ : non-linear demand curve.
Complete the correlation:
Ratio method : Ed = `(%triangle"Q")/(%triangle"P")` :: _______ : Ed = `"Lower segment"/"Upper segment"`
Explain the total outlay method of measuring elasticity of demand?
Assertion (A): Total expenditure method measures elasticity of demand at a given point on the demand curve.
Reasoning (R): Total expenditure refers to the product of price and quantity demanded.
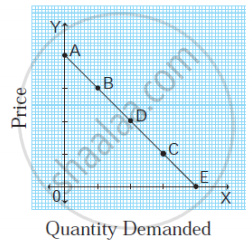
- Which method of measuring elasticity is used in above diagram? (1m)
- Mention the type of elasticity at point ‘C’? (1m)
- Find out the elasticity at point ‘D’ by applying formula (2m)
Explain the Total expenditure method and Geometric method of measuring price elasticity of demand.
Explain the Ratio method of measuring price elasticity of demand.
Complete the correlation:
Ratio method: Ed = `(%\Delta"Q")/(%\Delta"P")`:: ______ : Ed = `("Lower segment")/("Upper segment")`
Complete the correlation:
______ : Straight line demand curve : : Non-linear demand curve : Curved line demand curve
Ratio method : Ed = `(%ΔQ)/(%ΔP)` :: ______ : Ed = `("Lower segment")/("Upper segment")`
Ratio method: Ed = `(%Delta"Q") /(%Delta"UP")`:: ______: Ed = `("Lower segment")/ ("Upper segment")`
Complete the correlation:
Ratio method : Ed = `(%Δ Q) / (% Δ P)` :: ______ : Ed = `("Lower segment")/("Upper segment")`
Complete the correlation:
Ratio method : Ed = `(%ΔQ)/(%ΔP)` :: ______ : Ed = `"Lower segment"/"Upper segment"`
Complete the correlation :
Ratio method : Ed = `(%ΔQ)/(%ΔP)` :: _____ : Ed = `"Lower segment"/"Upper segment"`
Complete the correlation:
Ratio method : Ed = `(%ΔQ)/(%ΔP)` : : ______ : Ed = `("Lower segment")/("Upper segment")`
Complete the correlation:
Ratio method : Ed = `(%triangle"Q")/(%triangle"P")` :: _______ : Ed = `"Lower segment"/"Upper segment"`
Complete the correlation:
Ratio method : Ed = `("%"\Delta"Q")/("%"\Delta"P")` :: ______ : Ed =`("Lower segment") /("Upper segment")`
Complete the correlation:
Ratio method : Ed = `\(%Delta "Q") /(%\Delta "P"` :: ______ : Ed = `\("Lower segment")/("Upper segment")`
If demand increases by 50% due to an increase in price by 75%, calculate the price elasticity of demand.
The coefficient of price elasticity of a good is 0.8, its demand will said to be ______.
As a result of a 5% increase in price, the demand for commodity X increases by 12%. The price elasticity of demand will be ______.
The price of a commodity goes up from ₹ 26 to ₹ 30 as a result of which demand falls from 4 units to 2 units, the price elasticity of demand is ______.
Assertion (A): Suppose that a 2 per cent drop in the price of chocolate causes a 2 per cent increase in quantity demanded. This case is termed unit elasticity.
Reason (R): In this example, Ed is exactly 1 (or unity). Ed = `2/2=1`
Select the commodities from the following which have inelastic demand:
Is the demand for the following commodities elastic or inelastic?
- Salt
- Foodgrains
- Petrol
- Needles
- Green vegetables
- Four Square cigarettes
- Water
State the formula for calculating the price elasticity of demand using the percentage method.
The price of a commodity falls from ₹15 to ₹10. As a result, demand rises from 100 units to 150 units, Use the expenditure method to find the price elasticity of demand.
Study the table given below and state whether demand is elastic or inelastic. Give reasons for your answer.
| Price in (₹) | Total outlay (₹) |
| 5 | 25 |
| 3 | 18 |
The price of milk rises from ₹ 26.00 to ₹ 30.00 per litre and its demand falls from four litres per day to two litres per day. Calculate the elasticity demand for milk.
A consumer purchased 10 units of a commodity when its price was ₹ 5 per unit. He purchases 12 units of the commodity when price falls to ₹ 4 per unit. Calculate the price elasticity of demand for the commodity.
Give two examples of inelastic demand.
Give two examples of unitary elastic demand.
From the following state whether the price elasticity of demand is inelastic, relatively elastic, highly elastic or highly inelastic. Give reasons to support your answer.
demand for school uniform
From the following state whether the price elasticity of demand is inelastic, relatively elastic, highly elastic or highly inelastic. Give reasons to support your answer.
demand for refrigerators
From the following state whether the price elasticity of demand is inelastic, relatively elastic, highly elastic or highly inelastic. Give reasons to support your answer.
demand for electricity
From the following state whether the price elasticity of demand is inelastic, relatively elastic, highly elastic or highly inelastic. Give reasons to support your answer.
demand for cigar by a chain smoker
From the following state whether the price elasticity of demand is inelastic, relatively elastic, highly elastic or highly inelastic. Give reasons to support your answer.
demand for diesel and petrol
From the following state whether the price elasticity of demand is inelastic, relatively elastic, highly elastic or highly inelastic. Give reasons to support your answer.
demand for personal computers
From the following state whether the price elasticity of demand is inelastic, relatively elastic, highly elastic or highly inelastic. Give reasons to support your answer.
Demand for precious stones and costly jewellery
Ratio method : Ed = `(%ΔQ) /(%ΔP)` ______ :: Ed = `("Lower segment")/("Upper segment")`
