Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the types of stability with suitable examples.
उत्तर
Stability is a measure of the body’s ability to maintain its original position.
The three types of stability are
1. Stable Equilibrium:
The frustum can be tilted through quite a big angle without toppling.
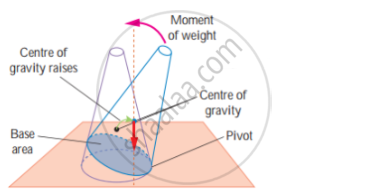
Its centre of gravity is raised when it is displaced. The vertical line through its centre of gravity still falls within its base. So it can return to its originalposition.
2. Unstable Equilibrium:
The frustum will topple with the slightest tilting. Its centre of gravity is lowered when it is displaced.
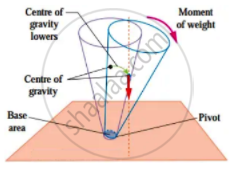
The vertical line through its centre of gravity falls outside its base.
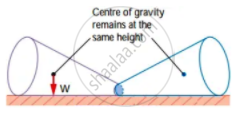
3. Neutral Equilibrium:
- It causes frustum to topple.
- The frustum will roll about but does not topple.
- Its centre of gravity remains at the same height when it is displaced.
- The body will stay in any position to which it has been displaced.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the condition when a body is in static equilibrium.
State the principle of moments. Give one device as an application of it
State two conditions for a body acted upon by several forces to be in equilibrium.
A meter scale is pivoted at its mid point and a 50 g mass suspended from the 20 cm mark. What mass balances the ruler when suspended from 65 cm mark?
Give scientific reason for the following:
When a man climbs a slope he bends forward.
Give scientific reason for the following:
In a moving bus the standing passenger stands keeping both his legs apart.
Give an experiment to verify the principle of moments.
How can we increase the stability of an object?
When a stone tied to a string is rotated in a horizontal plane, the tension in the string provides ______ force necessary for circular motion.
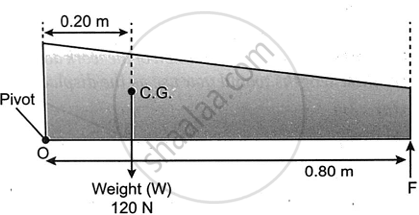
A non uniform beam of weight 120 N pivoted at one end is shown in the diagram below. Calculate the value of F to keep the beam in equilibrium.