Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the types of stability with suitable examples.
Solution
Stability is a measure of the body’s ability to maintain its original position.
The three types of stability are
1. Stable Equilibrium:
The frustum can be tilted through quite a big angle without toppling.
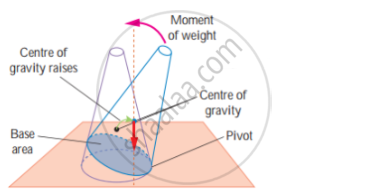
Its centre of gravity is raised when it is displaced. The vertical line through its centre of gravity still falls within its base. So it can return to its originalposition.
2. Unstable Equilibrium:
The frustum will topple with the slightest tilting. Its centre of gravity is lowered when it is displaced.
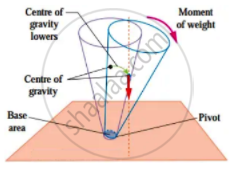
The vertical line through its centre of gravity falls outside its base.
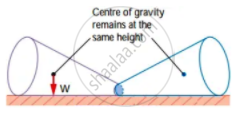
3. Neutral Equilibrium:
- It causes frustum to topple.
- The frustum will roll about but does not topple.
- Its centre of gravity remains at the same height when it is displaced.
- The body will stay in any position to which it has been displaced.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the condition when a body is in dynamic equilibrium.
State two condition for a body acted upon by several forces to be in equilibrium.
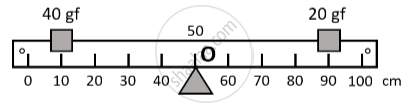
The figure shows a uniform metre rule placed on a fulcrum at its mid-point O and having a weight 40 gf at the 10 cm mark and a weight of 20 gf at the 90 cm mark.
- Is the metre rule in equilibrium? If not how will the rule turn?
- How can the rule be brought in equilibrium by using an additional weight of 40 gf?
A faulty balance of equal arms but pans of unequal weight is used to find the weight of a body. By the method of double weighing the weights are found as 8 kg and 8.2 kg. Find the actual weight of the body.
A faulty balance of unequal arms and pans of unequal weights is used to find the true weight of a metal. By double weighing the weights are found to be 1210 g and 1000 g. Calculate the true weight of the metal.
The moon revolving around the earth is in ______ equilibrium.
Explain when we carry weight, on one hand, we bend on the other side.
What is the weight of a body placed at the centre of the earth?
One end of a spring is kept fixed while the other end is stretched by a force as shown in the diagram.
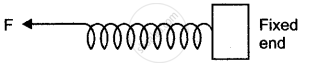
(i) Copy the diagram and mark on it the direction of the restoring force.
(ii) Name one instrument which works on the above principle.
