Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain why covalent compounds have generally high melting points?
उत्तर
Covalent compounds are made up of electrically neutral molecules. So the force of attraction between the molecules is very weak. Only a small amount of heat energy is required to break these weak molecular forces, due to which covalent compounds have a low melting point.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What type of bond exist in CCl4?
What type of chemical bonds are formed by carbon? Why?
Explain why, diamond can be used in rock drilling equipment but graphite cannot.
Explain why, diamond has a high melting point.
For each compound mentioned above give the formulae of ions formed in aqueous solution.
Which element exhibits the property of catenation to maximum extent and why?
Draw an electron dot structure of the following molecule. (Without showing the circle) :
Methane
Explain the following term with example.
Unsaturated hydrocarbon
The following structural formula belongs to which carbon compound?
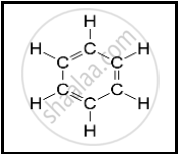
Choose and write the correct option.
Which type of carbon-carbon bonds are present in Vanaspati ghee?
Which of the following is a common characteristic of a covalent compound?
Element A has 2 electrons in its M shell. Element B has atomic number 7.
Write equations to show how A and B form ions.
Taking MgCl2 as an electrovalent compound, CCl4 as a covalent compound, give four difference between electrovalent and covalent compounds
Name the anion present in the following compound:
When a barium chloride solution is added to a solution of compound B, a white precipitate insoluble in dilute hydrochloric acid is formed.
Complete the following activity.
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
| \[\begin{array}{cc}\phantom{......}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{..}\\ \phantom{.....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\ \ce{H - C - C = C}\\\phantom{.....}|\phantom{.........}|\\ \phantom{.....}\ce{H}\phantom{........}\ce{H}\end{array}\] |
Identify the incorrect statement and correct them.
- Like covalent compounds, coordinate compounds also contain charged particles (ions). So they are good conductors of electricity.
- Ionic bond is a weak bond when compared to Hydrogen bond.
- Ionic or electrovalent bonds are formed by mutual sharing of electrons between atoms.
- Loss of electrons is called Oxidation and gain of electron is called Reduction.
- The electrons which are not involved in bonding are called valence electrons.
Which of the following is the purest form of carbon?
Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane?
- \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{.....}|\phantom{.....}|\\
\ce{H}\ce{H-C-H}\ce{H}\\
|\\
\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{.....}\backslash\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{H}\phantom{......}\ce{C - H}\phantom{}\\
\phantom{.......}|\\
\phantom{.......}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\]
In covalent compounds, the bond is formed due to ______ of electrons.
