Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain with examples types of asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms.
उत्तर
Asexual reproduction occurs in unicellular organisms through various methods. Some of these methods are as follows:
- Binary Fission: In this method, the parent cell divides into two equal parts, resulting in the formation of two new daughter cells. This division occurs through mitotic division. Generally, binary fission occurs in favourable conditions when sufficient food is available. Bacteria, protozoa, mitochondria, and chloroplasts reproduce asexually through binary fission.
Depending on the axis of division, binary fission in different protozoa is classified as:- Simple Binary Fission: Since Amoeba does not have a definite shape, it can divide along any axis. Therefore, this type of fission is called simple binary fission.
Example: Amoeba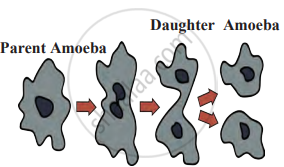
- Transverse (Horizontal) Binary Fission: In Paramecium, division occurs along the transverse axis.
Example: Paramecium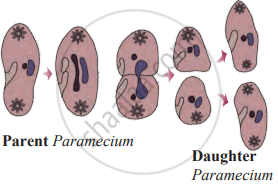
- Longitudinal (Vertical) Binary Fission: In Euglena, division occurs along the longitudinal axis.
Example: Euglena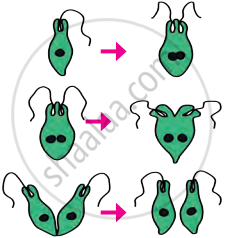
- Simple Binary Fission: Since Amoeba does not have a definite shape, it can divide along any axis. Therefore, this type of fission is called simple binary fission.
- Multiple Fission: Amoeba and similar unicellular protozoa reproduce asexually through multiple fission in unfavourable conditions. When food is insufficient or environmental conditions become unfavourable, Amoeba stops moving and does not produce pseudopodia. It becomes spherical and forms a hard protective covering around itself, known as a "Cyst."
Inside the cyst, the nucleus undergoes multiple mitotic divisions, resulting in the formation of several nuclei. Later, the cytoplasm also divides, producing multiple small Amoebae. These remain inside the cyst until favourable conditions return. Once conditions improve, the cyst bursts, releasing several young Amoebae.
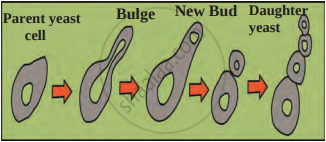
- Budding: Yeast reproduces asexually through budding. First, mitotic division occurs in the parent cell, producing two daughter nuclei. A small outgrowth, called a "Bud," appears on the parent cell. One of the daughter nuclei enters this bud. After growing sufficiently, the bud detaches from the parent cell and starts developing as an independent yeast cell.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Put a tick mark (✓) against the correct alternative in the following statement:
Internally, the uterus opens into:
Complete the paragraph with the help of words given in the bracket.
(Luteinizing hormone, endometrium of uterus, follicle stimulating hormone, estrogen, progesterone, corpus luteum)
Growth of follicles present in the ovary occurs under the effect of ____________. This follicle secretes estrogen. _____________ grows/regenerates under the effect of estrogen. Under the effect of ___________, fully grown up follicle bursts, ovulation occurs and _______________ is formed from remaining part of follicle. It secrets ____________ and __________. Under the effect of these hormones, glands of ____________ are activated and it becomes ready for implantation.
After puberty human female shows cyclic changes in her reproductive system. Explain structural and hormonal changes in the uterus.
(OR)
Give reasons :
(1) Scrotal sac serves as thermoregulator.
(2) Corpus luteum gets converted into corpus albicans in absence of fertilization.
(3) Missing of menses is the first indication of pregnancy.
(4) Surgical sterilization is a permanent method of birth control. (5) Human egg is microlecithal.
Give appropriate term of the following:
The monthly discharge of blood and disintegrated uterine tissues in human female.
Define the following:
Parturition
Give Technical Term:
What term is used for the production and maturation of eggs in the ovaries?
Complete the following sentences with appropriate word:
The female equivalent of the penis is the _______.
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
The cilia lining the oviduct funnel, push the released ovum into the uterus.
The largest cell in the human body of a female is ______.
What is the other term used for fallopian tube?
Development of mammary glands is controlled by ____________.
Mark the CORRECT sequence of structures in the breast from the inner to the outer side.
Egg is liberated from ovary in ______.
Extra-embryonic membranes of the mammalian embryo are derived from ______.
Read the following and answer from given below:
During copulation, semen is released by the penis into the vegina. The motile sperms swim rapidly, fuse with the ovum in the ampullary region, resulting in fertilization. The haploid nucleus of sperm fuses with that of the ovum to form a diploid zygote.
In the female genital tract, sperms are made capable of fertilizing the egg. This phenomenon of sperm activation is called ______
In which part of the human female reproductive system do the following events take place?
Release of second polar body
Give reason.
Placenta is extremely essential for foetal development.
The ______ is also called the womb.
Distinguish between the following pair:
Spermatogenesis and oogenesis
The figure given below is the human female reproductive system. Study the same and answer the following questions.
 |
- Label the guidelines 1 to 6 shown in the figure.
- What is the normal gestation period in human?
- Where are the sperms released during coitus?
- Write two important functions of part 2.
- Mention the technical term for the fixing of developing zygote to the uterine wall.
