Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain with examples types of asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms.
Solution
Asexual reproduction occurs in unicellular organisms through various methods. Some of these methods are as follows:
- Binary Fission: In this method, the parent cell divides into two equal parts, resulting in the formation of two new daughter cells. This division occurs through mitotic division. Generally, binary fission occurs in favourable conditions when sufficient food is available. Bacteria, protozoa, mitochondria, and chloroplasts reproduce asexually through binary fission.
Depending on the axis of division, binary fission in different protozoa is classified as:- Simple Binary Fission: Since Amoeba does not have a definite shape, it can divide along any axis. Therefore, this type of fission is called simple binary fission.
Example: Amoeba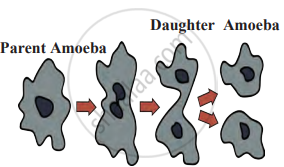
- Transverse (Horizontal) Binary Fission: In Paramecium, division occurs along the transverse axis.
Example: Paramecium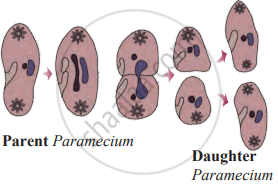
- Longitudinal (Vertical) Binary Fission: In Euglena, division occurs along the longitudinal axis.
Example: Euglena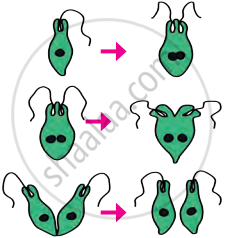
- Simple Binary Fission: Since Amoeba does not have a definite shape, it can divide along any axis. Therefore, this type of fission is called simple binary fission.
- Multiple Fission: Amoeba and similar unicellular protozoa reproduce asexually through multiple fission in unfavourable conditions. When food is insufficient or environmental conditions become unfavourable, Amoeba stops moving and does not produce pseudopodia. It becomes spherical and forms a hard protective covering around itself, known as a "Cyst."
Inside the cyst, the nucleus undergoes multiple mitotic divisions, resulting in the formation of several nuclei. Later, the cytoplasm also divides, producing multiple small Amoebae. These remain inside the cyst until favourable conditions return. Once conditions improve, the cyst bursts, releasing several young Amoebae.
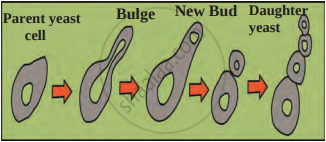
- Budding: Yeast reproduces asexually through budding. First, mitotic division occurs in the parent cell, producing two daughter nuclei. A small outgrowth, called a "Bud," appears on the parent cell. One of the daughter nuclei enters this bud. After growing sufficiently, the bud detaches from the parent cell and starts developing as an independent yeast cell.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a labelled diagram of female reproductive system.
State the function of Fallopian tubes.
Rewrite the terms in the correct order so as to be in a logical sequence.
Puberty, menopause, menstruals, menarche, reproductive age.
Sketch the labeled diagram:
Human female reproductive system
Modern techniques like surrogate mother, sperm bank and IVF technique will help the human beings. Justify this statement.
Mention the exact location of the following :
Amniotic fluid
Mention the exact location of the following :
Corpus callosum
Name the Following
The structure formed after the release of ovum from the Graffian follicle.
The _______ is also called the womb.
What is true of gametes?
______ pollen mother cells should undergo meiotic division to produce 64 pollen grains.
Identify the layer that makes up the corona radiate.
Identify the layer of the uterine wall that undergoes changes during menstrual cycle.
A sac shaped like an upside down pear with a thick lining and muscles in the pelvic area where a fertilized egg or zygote comes to grow into a baby is called ______.
Read the following and answer from given below:
Oogenesis is the process of the formation of an ovum in the ovaries. It consists of three phases: multiplication, growth, and maturation. Oogenesis is controlled by hormones GnRH, LH, FSH. GnRH secreted by the hypothalamus stimulates the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland to secrete LH and FSH.
what is the function of hormones FSH?
The oviducts are also known as ______.
______ receives the sperms and acts as a birth canal during childbirth.
Match the following:
| Ovaries | Bean shape |
| Fallopian tubes | Almond shape |
| Uterus | Funnel – shape |
| Kidney | pear-shaped |
Bartholin's glands are homologous to ______.
Write the specific location of the following:
Vagina
