Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain with reasons and diagrams, the positive and negative deviations from Raoult’s law shown by nonideal solutions.
उत्तर
- Positive deviation from Raoult’s law:
The solutions in which solute-solvent intermolecular attractions are weaker than those between solute-solute molecules and solvent-solvent molecules, exhibit positive deviations. The vapour pressures of such solutions are higher than those of pure components as shown in the diagram.
e.g. The solutions of ethanol + acetone, carbon disulphide + acetone show positive deviations from Raoult’s law.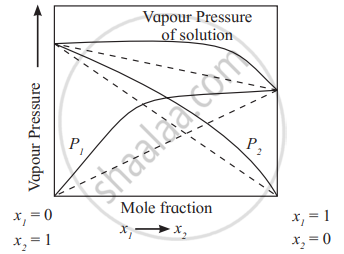
Positive derivations from Raoult's law - Negative deviation from Raoult’s law:
The solutions in which the interactions between solvents and solute molecules are stronger than solute-solute or solvent-solvent interactions, exhibit negative deviations. The vapour pressures of such solutions are lower than those of pure components as shown in the diagram.
e.g. Solutions of phenol + aniline, chloroform + acetone exhibit negative deviations from Raoult’s law.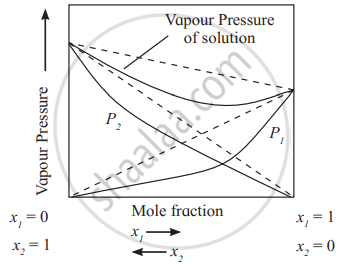
Negative derivations from Raoult's law
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the most correct option.
The vapour pressure of a solution containing 2 moles of a solute in 2 moles of water (vapour pressure of pure water = 24 mm Hg) is ______.
Answer the following.
Using Raoult’s law, how will you show that ΔP = `"P"_1^0 "x"_2`? Where, x2 is the mole fraction of solute in the solution and `"P"_1^0` vapour pressure of pure solvent.
The vapour pressure of water at 20°C is 17 mm Hg. What is the vapour pressure of solution containing 2.8 g urea in 50 g of water?
What type of solutions exhibit positive deviations from Raoult’s law?
What is enthalpy change and volume change of mixing of two components forming an ideal solution?
The vapour pressures of pure liquids A and B are 0.600 bar and 0.933 bar respectively, at a certain temperature.
What is the mole fraction of liquid B in the solution when the total vapour pressure of their mixture is 0.8 bar?
Distinguish between ideal and non-ideal solutions.
What are nonideal solutions?
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
Which of the following metals is refined by vapour phase refining in Mond process?
Which of the following is NOT nonideal solution?
If 1 mole of ____________ is added to 1 dm3 of water, the boiling point of water will decrease.
5.0 g of sodium hydroxide (molar mass 40 g mol-1) is dissolved in little quantity of water and the solution is diluted upto 100 mL. What is the molarity of the resulting solution?
A solution of acetone in ethanol ______.
18 g of glucose (C6H12O6) is added to 178.2 g of water. The vapour pressure of water for this aqueous solution is ______.
For an ideal binary liquid solution with `"p"_"A"^circ > "P"_"B"^circ`, which is a relation between XA (mole fraction of A in liquid phase) and YA (mole fraction of A in vapour phase) is correct, XB and YB are mole fractions of B in liquid and vapour phase respectively?
Total vapour pressure of a mixture of 1 mole A`("p"_"A"^circ = 150 " torr")` and 2 mole B`("p"_"B"^circ = 240 " torr")` is 200 mm. In this case, ______.
What are ideal and non-ideal solutions?
A solution having highest vapour pressure is ______.
Explain the variation of vapour pressures with mole fractions of binary solutions of two volatile liquids forming ideal solutions.
State Raoult's law for solutions of volatile components.
A mixture of two liquids A and B have vapour pressures 3.4 × 104 Mn-2 and 5.2 × 104 Nm-2. If the mole fraction of A is 0.85, find the vapour pressure of the solution.
