Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain with reasons and diagrams, the positive and negative deviations from Raoult’s law shown by nonideal solutions.
उत्तर
- Positive deviation from Raoult’s law:
The solutions in which solute-solvent intermolecular attractions are weaker than those between solute-solute molecules and solvent-solvent molecules, exhibit positive deviations. The vapour pressures of such solutions are higher than those of pure components as shown in the diagram.
e.g. The solutions of ethanol + acetone, carbon disulphide + acetone show positive deviations from Raoult’s law.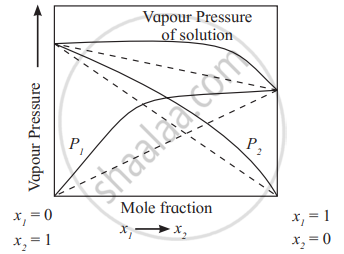
Positive derivations from Raoult's law - Negative deviation from Raoult’s law:
The solutions in which the interactions between solvents and solute molecules are stronger than solute-solute or solvent-solvent interactions, exhibit negative deviations. The vapour pressures of such solutions are lower than those of pure components as shown in the diagram.
e.g. Solutions of phenol + aniline, chloroform + acetone exhibit negative deviations from Raoult’s law.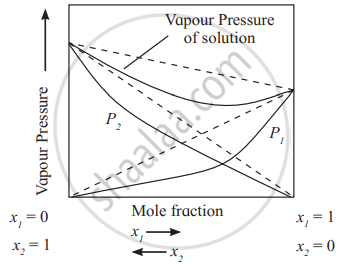
Negative derivations from Raoult's law
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the most correct option.
The vapour pressure of a solution containing 2 moles of a solute in 2 moles of water (vapour pressure of pure water = 24 mm Hg) is ______.
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
State Raoult’s law for a solution containing a nonvolatile solute.
Answer the following.
Using Raoult’s law, how will you show that ΔP = `"P"_1^0 "x"_2`? Where, x2 is the mole fraction of solute in the solution and `"P"_1^0` vapour pressure of pure solvent.
Fish generally needs O2 concentration in water at least 3.8 mg/L for survival. What partial pressure of O2 above the water is needed for the survival of fish? Given the solubility of O2 in water at 0 °C and 1 atm-1 partial pressure is 2.2 × 10-3 atm mol/L.
The vapour pressure of water at 20°C is 17 mm Hg. What is the vapour pressure of solution containing 2.8 g urea in 50 g of water?
State Raoult’s law.
What type of solutions exhibit positive deviations from Raoult’s law?
Distinguish between ideal and non-ideal solutions.
What are nonideal solutions?
Which of the following metals is refined by vapour phase refining in Mond process?
Which of the following is NOT nonideal solution?
9 gram anhydrous oxalic acid (mol. wt. = 90) was dissolved in 9.9 moles of water. If vapour pressure of pure water is pf the vapour pressure of solution is ______.
A solution of acetone in ethanol ______.
18 g of glucose (C6H12O6) is added to 178.2 g of water. The vapour pressure of water for this aqueous solution is ______.
What are ideal and non-ideal solutions?
The vapour pressures of two liquids A and B are 80 mmHg and 60 mm Hg respectively at 25°C. What is the vapour pressure of the solution obtained by mixing 3 moles of A and 2 moles of B?
State Raoult's law for solutions of volatile components.
Write the relationship between mole fraction of solvent and vapour pressure of solution.
A mixture of two liquids A and B have vapour pressures 3.4 × 104 Mn-2 and 5.2 × 104 Nm-2. If the mole fraction of A is 0.85, find the vapour pressure of the solution.
The solutions that obey Raoult's law over entire range of concentrations are ______.
