Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain with vapour pressure-temperature curves that the freezing point of a solvent is lowered by dissolving a nonvolatile solute into it. Give reason for such lowering of freezing of solvent.
उत्तर
- The vapour pressures of solution and of pure solvent are plotted as a function of temperature in the diagram.
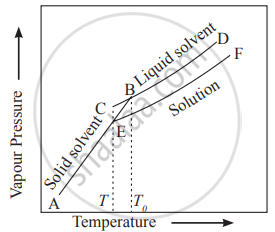
Variation of vapour pressure with a temperature of pure solvent, solid solvent and solution - The diagram consists of three curves. AB is the vapour pressure curve of solid solvent while CD is the vapour pressure curve of pure liquid solvent. EF is the vapour pressure curve of solution that always lies below the pure solvent.
- The curves AB and CD intersect at point B where solid and liquid phases of pure solvent are in equilibrium. The two phases have the same vapour pressure at B. The temperature corresponding to B is the freezing point of a solvent `("T"_"f"^0)`.
- Similarly at E, the point of intersection of EF and AB, the solid solvent and solution are in equilibrium. They have the same vapour pressure at E. The temperature corresponding to E is the freezing point of a solution `("T"_"f")`.
- It is clear from the diagram that freezing point of solution `("T"_"f")` is lower than that of pure solvent `("T"_"f"^0)` because the vapour pressure curve of solution lies below that of solvent.
- Reason for lowering of freezing of the solvent:
At the freezing point of a pure liquid, the attractive forces among molecules are large enough to cause the change of phase from liquid to solid. In a solution, the solvent molecules are separated from each other because of solute molecules. Thus, the separation of solvent molecules in solution is more than that in pure solvent. This results in decreasing the attractive forces between solvent molecules. Consequently, the temperature of the solution is lowered below the freezing point of the solvent to cause the phase change. Hence, freezing point of solvent is lowered by dissolving a nonvolatile solute into it.
संबंधित प्रश्न
An aqueous solution of urea freezes at – 0.186°C, Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mo1–1, Kb for water = 0.512 K kg mo1–1. The boiling point of urea solution will be:
Ethylene glycol is used as an antifreeze agent. Calculate the amount of ethylene glycol to be added to 4 kg of water to prevent it from freezing at -6°C. (Kf for H2O = 1 .85 K mole-1 kg)
Answer the following question:
Why the freezing point depression (ΔTf) of 0.4 M NaCl solution is nearly twice than that of 0.4 M glucose solution?
Obtain the relationship between freezing point depression of a solution containing nonvolatile-nonelectrolyte solute and its molar mass.
A 5% aqueous solution (by mass) of cane sugar (molar mass 342 g mol-1) has a freezing point of 271 K. Calculate the freezing point of 5% aqueous glucose solution.
Freezing point depression constant of a solvent is _______.
What is a cryoscopic constant?
Write the effect of dissolution of a nonvolatile solute on the freezing point of solvent.
Calculate total moles after dissociation in 0.1 M KCl solution and 0.05 M aluminium sulphate solution. Hence, decide which of the two solutions will have higher freezing point depression.
Write the SI unit of the cryoscopic constant.
At the freezing point ______.
Derive the equation for the molar mass of solute from freezing point depression.
Calculate the mass of compound to be dissolved in 75g of benzene to lower its freezing point by 0.48 K. (Given: Kf = 0.512 K kg mol-1 and molar mass = 256g mol-1)
Calculate the mass of ascorbic acid (molecular mass = 176 g/mol) that should be dissolved in 155 g of acetic acid to cause a depression of the freezing point by 1.15 K. Assume that ascorbic acid does not dissociate or associate in the solution. (Kf for acetic acid = 3.9 K kg/mol)
Ethylene glycol is used as an antifreeze agent. Calculate the amount of ethylene glycol to be added to four kilogram of water to prevent it from freezing at −6°C.
(Kf of water = 1.86 K kg mol-1 ) Assume that ethylene glycol (CH2OH.CH2OH) does not dissociate or associate in aqueous solution.
