Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
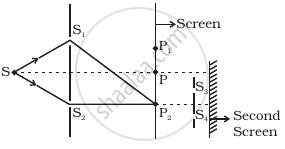
Figure shows a standard two slit arrangement with slits S1, S2, P1, P2 are the two minima points on either side of P (Figure). At P2 on the screen, there is a hole and behind P2 is a second 2-slit arrangement with slits S3, S4 and a second screen behind them.
विकल्प
There would be no interference pattern on the second screen but it would be lighted.
The second screen would be totally dark.
There would be a single bright point on the second screen.
There would be a regular two slit pattern on the second screen.
उत्तर
There would be a regular two slit pattern on the second screen.
Explanation:
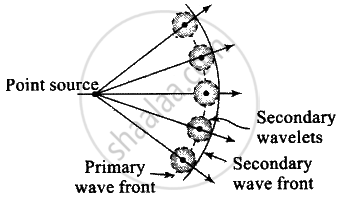
Every point on the given wave front acts as a source of new disturbance called secondary wavelets which travel in all directions with the velocity of light in the medium.
A surface touching these secondary wavelets tangentially in the forward direction at any instant gives the new wavefront at that instant. This is called secondary wavefront. In the given question, there is a hole at point which is a maxima point. From Huygen’s principle, wave will propagate from the sources S1 and S2. Each point on the screen will act as secondary source of wavelets.
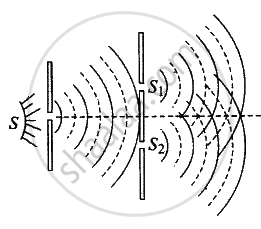
The wavefront emitted by a narrow source is divided into two parts reflection, refraction or diffraction. The coherent sources so obtained are imaginary.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Using Huygens's construction of secondary wavelets explain how a diffraction pattern is obtained on a screen due to a narrow slit on which a monochromatic beam of light is incident normally.
What is the shape of the wavefront in the following case?
Light diverging from a point source.
Using this principle draw a diagram to show how a plane wave front incident at the interface of the two media gets refracted when it propagates from a rarer to a denser medium. Hence verify Snell's law of refraction.
State Huygens’s principle. Show, with the help of a suitable diagram, how this principle is used to obtain the diffraction pattern by a single slit.
Draw a plot of intensity distribution and explain clearly why the secondary maxima becomes weaker with increasing order (n) of the secondary maxima.
Light waves travel in vacuum along the X-axis. Which of the following may represent the wave fronts?
Define the term wavefront. Using Huygen’s wave theory, verify the law of reflection.
According to Huygens principle, ______.
Using Huygen's wave theory of light, show that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Draw a neat and labelled diagram.
What type of wavefronts are associated with a point source of light?
Represent diagrammatically how the incident planar wavefronts of wavelength λ pass through an aperture of size d, when d is approximately equal to λ.
