Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Fill in the blanks using the word(s) from the list appended with each statement
For solids with elastic modulus of rigidity, the shearing force is proportional to . . . , while for fluids it is proportional to . .. (shear strain / rate of shear strain)
उत्तर
Shear strain; Rate of shear strain
With reference to the elastic modulus of rigidity for solids, the shearing force is proportional to the shear strain. With reference to the elastic modulus of rigidity for fluids, the shearing force is proportional to the rate of shear strain.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
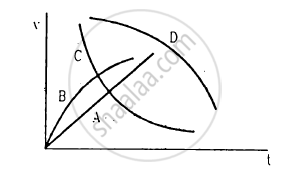
A spherical ball is dropped in a long column of a viscous liquid. The speed of the ball as a function of time may be best represented by the graph
A metal sphere of radius 1 mm and mass 50 mg falls vertically in glycerine. Find (a) the viscous force exerted by the glycerine on the sphere when the speed of the sphere is 1 cm s−1, (b) the hydrostatic force exerted by the glycerine on the sphere and (c) the terminal velocity with which the sphere will move down without acceleration. Density of glycerine = 1260 kg m−3 and its coefficient of viscosity at room temperature = 8.0 poise.
Water flows at a speed of 6 cm s−1 through a tube of radius 1 cm. Coefficient of viscosity of water at room temperature is 0.01 poise. Calculate the Reynolds number. Is it a steady flow?
Analogy
Viscous force: ______:: Buoyant force: ______.
Clouds float in the air due to ______.
A spherical solid ball of volume V is made of a material of density ρ1. It is falling through a liquid of density ρ2 (ρ2 < ρ1). Assume that the liquid applies a viscous force on the ball that is proportional to the square of its speed v, i.e., `"F"_"viscous"`= -kv2 (k > 0). The terminal speed of the ball is ______.
The coefficient of apparent expansion of mercury in a glass vessel is 153 × 10-6/°C and in a steel vessel is 144 × 10-6/°C. If α for steel is 12 × 10-6/°C, then that of glass is ______.
Define velocity gradient.
An incompressible liquid is flowing through a uniform cross-sectional tube with a velocity 12 cm/ s. If the thickness of liquid layer is 0.8 cm, what is the velocity gradient of that flow of liquid?
A water pipe with diameter of 5.0 cm is connected to another pipe of diameter 2.5 cm. How would the speeds of the water flow compare?
