Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The photoelectric work function for a metal surface is 2.3 eV. If the light of wavelength 6800A is incident on the surface of metal, find threshold frequency and incident frequency. Will there be an emission of photoelectrons or not?
[Velocity of light c = 3 x 108 m/s,
Planck’s constant, h = 6.63 * 10-34 Js ]
उत्तर
Given:
`phi_0=2.3 eV=2.3*1.6*10^-19 J=3.68*10^-19J`
λ=6800 Å=6800*10-10m, c=3*108 m/s, h=6.63*10-34 Js
We know that the incident frequency is given as
`v=c/lambda`
∴`v=(3*10^8)/(6800*10^-10)=4.41*10^14Hz`
Now, if the incident frequency is greater than the threshold frequency, then photoelectrons will be emitted from the metal surface. The threshold frequency is given from work function as
`v_0=phi_0/h`
`v_0=(3.68*10^-19)/(6.63*10^-34)=5.55*10^14Hz`
Since, photoelectrons `v<v_0` will not be emitted.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a neat labelled circuit diagram of experimental arrangement for study of photoelectric effect.
Write three characteristic features in photoelectric effect that cannot be explained on the basis of wave theory of light, but can be explained only using Einstein's equation.
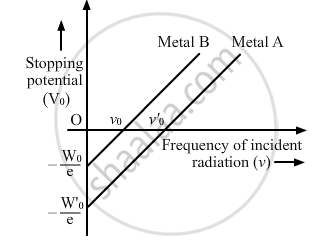
Sketch the graphs showing variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident radiations for two photosensitive materials A and B having threshold frequencies vA > vB.
(i) In which case is the stopping potential more and why?
(ii) Does the slope of the graph depend on the nature of the material used? Explain.
Light of intensity ‘I’ and frequency ‘v’ is incident on a photosensitive surface and causes photoelectric emission. What will be the effect on anode current when (ii) the frequency of incident radiation is increased. In each case, all other factors remain the same. Explain, giving justification in each case.
Light of intensity ‘I’ and frequency ‘v’ is incident on a photosensitive surface and causes photoelectric emission. What will be the effect on anode current when the anode potential is increased? In each case, all other factors remain the same. Explain, giving justification in each case.
Two monochromatic beams, one red and the other blue, have the same intensity. In which case (i) the number of photons per unit area per second is larger, (ii) the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is more? Justify your answer.
The graph shows the variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident radiation for two photosensitive metals A and B. Which one of the two has higher value of work-function? Justify your answer.
The work functions for potassium and caesium are 2.25 eV and 2.14 eV respectively. Is the photoelectric effect possible for either of them if the incident wavelength is 5180 Å?
[Given : Planck’s constant = 6.63 x 10–34 J.s.;
Velocity of light = 3 x 108 m/s; 1 eV = 1.6 x 10–19 J]
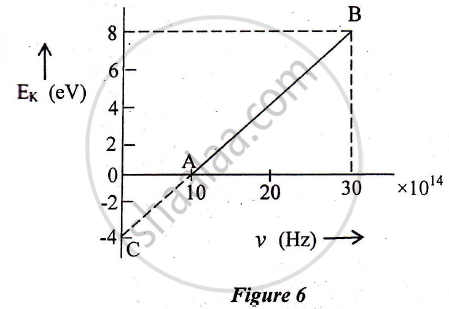
In an experiment of the photoelectric effect, the graph of maximum kinetic energy EK of the emitted photoelectrons versus the frequency v of the incident light is a straight line AB shown in Figure 6 below:
Find:
1) Threshold frequency of the metal
2) The work function of the metal.
3) Stopping potential for the photoelectrons emitted by the light of frequency `v = 30 xx 10^14 Hz`
A beam of monochromatic radiation is incident on a photosensitive surface. Answer the following question giving reason :
Do the emitted photoelectrons have the same kinetic energy?
A beam of monochromatic radiation is incident on a photosensitive surface. Answer the following question giving reason :
Does the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons depend on the intensity of incident radiation?
A beam of monochromatic radiation is incident on a photosensitive surface. Answer the following question giving reason :
On what factors does the number of emitted photoelectrons depend?
In photoelectric effect, why should the photoelectric current increase as the intensity of monochromatic radiation incident on a photosensitive surface is increased? Explain.
What is photoelectri effect ? Defin (i) Stopping potential (ii) Photoelectric work function.
Calculate the momentum of a photon of energy 6 x I 0-19 J.
With reference to the photoelectric effect, what is meant by threshold wavelength?
Two metals A and B have work functions 4 eV and 6 eV respectively. Which metal has a lower threshold wavelength for photoelectric effect?
Plot a labelled graph of IVsl where Vs is stopping potential versus frequency f of the incident radiation.
State how will you use this graph to detennine the value of Planck's constant.
If the frequency of the incident radiation is increased from 4 × 1015 Hz to 8 × 1015 Hz, by how much will the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface go up?
Photoelectric effect is possible ______.
Light of wavelength 4000 Å is incident on two metals A and B. Which metal will emit photoelectrons, if their work functions are 3.8 e V and 1.6 e V respectively?
