Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give the main function of the following:
Fovea centralis
उत्तर
Fovea centralis - It is a point at retina where more cone cells are concentrated and thus produces sharpest vision.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The eyes of a person are focused (i) on a nearby object, and (ii) on a distant object, turn by turn. In which case:
the focal length of eye-lens will be the maximum?
There are two types of light-sensitive cells in the human eye:
Where are they found?
How does the convex eye-lens differ from the ordinary convex lens made of glass?
Five persons A, B, C, D and E have diabetes, leukaemia, asthma, meningitis and hepatitis, respectively.
Which of these persons cannot donate eyes?
Name the respective organs in which the following are located and mention the main function of each:
(i) Iris
(ii) Semicircular canals
Name the following:
The opening through which light enters the eyes.
Choose the correct answer.
In the chemistry of vision, the photosensitive substance is _________________
Answer the following question.
Write the structure of eye lens and state the role of ciliary muscles in the human eye.
Differentiate between:
Yellow spot and Blind spot.
Give Technical Term:
The cells of the retina that are sensitive to colour.
Give Technical Term:
Name the part of the retina on which an object is focused for the clearest vision.
Give Technical Term:
The nutritive layer of the eye which also presents reflection of light.
Mention, if the following statement is True or False
Cones are the receptor cells in the retina of the eye sensitive to dim light.
Write scientific reason.
The movie cannot be enjoyed if seat of a viewer is too close to the screen in the cinema.
A student sitting on the last bench can read the letters written on the blackboard but is not able to read the letters written in his text book. Which of the following statements is correct?
A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light is incident on the prism as shown in Figure . In which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky?
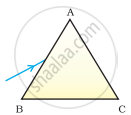 |
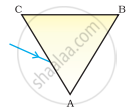 |
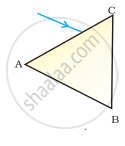 |
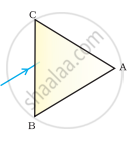 |
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) |
We cannot distinguish colours in dim light. Explain giving suitable reasons.
Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Answer the questions that follow:
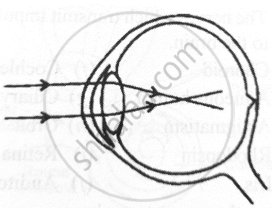
- Give the scientific term for the defect.
- Mention one possible reason for the defect.
- What type of lens can be used to correct the defect?
State the functions of the following:
Iris
The thin, transparent extension of sclerotic layer found in front of the lens is ______.
