Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
We cannot distinguish colours in dim light. Explain giving suitable reasons.
उत्तर
Rods are abundantly found in the retina and are sensitive to dim light. Rods also detect changes in the intensity of light across the field of vision and thus aid in the perception of movement. Rods do not play a role in distinguishing colour, and cones are insensitive to dim light. That is why colours can't be seen in dim light.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The region of the vertebrate eye, where the optic nerve passes out of the retina, is called the
(a) fovea
(b) iris
(c) blind spot
(d) optic chaisma
What changes the shape of lens in the eye?
How is the amount of light entering the eye controlled?
Describe the working of the human eye with the help of the above diagram.
Refraction of light in the eye occurs at:
(a) the lens only
(b) the cornea only
(c) both the cornea and the lens
(d) the pupil
How does the eye change in order to focus on near or distant objects?
(a) The lens moves in or out
(b) The retina moves in or out
(c) The lens becomes thicker or thinner
(d) The pupil gets larger or smaller
What shape are your eye-lenses:
when you look at a distant tree?
State whether the following statement is true or false:
Rabbit has eyes which look sideways.
State the function of each of the following parts of the human eye:
(i) Cornea
(ii) Iris
(iii) Pupil
(iv) Retina
Millions of people of the developing countries are suffering from corneal blindness. This disease can be cured by replacing the defective cornea with the cornea of a donated eye. Your school has organised a campaign in the school and its neighbourhood in order to create awareness about this fact and motivate people to donate their eyes after death. How can you along with your classmates contribute in this noble cause? State the objectives of organising such campaigns in schools.
Define the following:
Yellow spot
Name the following:
The opening through which light enters the eyes.
Draw a diagram of the human eye as seen in a vertical section and label the parts which suit the following descriptions relating to the:
(i) photosensitive layer of the eye.
(ii) structure which is responsible for holding the eye lens in its position.
(iii) structure which maintains the shape of the eyeball and the area of no vision.
(iv) anterior chamber seen in front of the eye lens.
(v) outermost transparent layer seen in front of the eyeball.
What is the nature of the image that forms on the retina?
Write an Explanation.
Power of accommodation
Assertion: Blind spot is a small area of the retina which is insensitive to light where the optic nerve leaves the eye.
Reason: There are no rods or cones present at the junction of the optic nerve and retina in the eye.
Explain the structure and functioning of Human eye. How are we able to see nearby as well as distant objects?
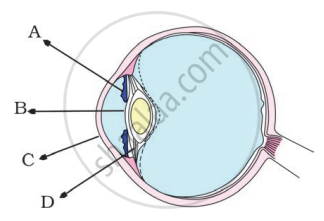
In the figure of the human eye, the cornea is represented by the letter
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| 1. Retina | a) Path way of light |
| 2. Pupil | b) Far point comes closer |
| 3. Ciliary muscles | c) near point moves away |
| 4. Myopia | d) Screen of the eye |
| 5. Hypermetropia | e) Power of accommodation |
Explain the role of the part of human eye responsible for power of accommodation of human eye.
Arrange and rewrite the term in group in correct order to be in a logical sequence, beginning with the term that is underlined:
Pupil, Aqueous humour, Retina, Vitreous humour.
