Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give three uses of ethene.
उत्तर
Three uses of ethene are:
1. It is used for the manufacture of polythene
2. For the artificial ripening of fruits.
3. As a general anaesthetic.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The equation for the reaction when compound A is bubbled through bromine dissolved in carbon tetrachloride is as follows:
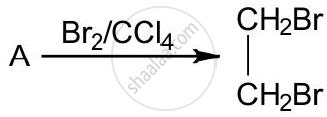
1) Draw the structure of A.
2) State your observation during this reaction.
Give the name and formulae of one member of each of the following:
(a) Saturated hydrocarbons
(b) Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
The first organic compound prepared by Wohler in the laboratory was
Write the equation of the following laboratory preparation:
Ethene from iodoethane
Compound A is bubbled through bromine dissolved in carbon tetrachloride, and the product is CH2Br - CH2Br.
\[\ce{A ->[Br2/CCl4] CH2Br - CH2Br}\]
- Draw the structural formula of A.
- What type of reaction has A undergone?
- What is your observation?
- Name (not formula) the compound formed when steam reacts with A in the presence of pliosphoric acid.
- What is the procedure for converting the product of (iv) back to A?
Identify the gas evolved when sodium propionate is heated with sodalime
Identify the term or substance based on the descriptions given below:
The property by virtue of which the compound has the same molecular formula but different structural formulae.
Compound X bubbled through bromine dissolved in carbon tetrachloride CCl4;
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{X ->[Br2CCl4] CH2Br}\\
\phantom{......}|\\
\phantom{...........}\ce{CH2Br}\\
\end{array}\]
Draw the structure of X.
Give the IUPAC name of the organic compound represented by the structural formula given below:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{Cl}\phantom{..}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{Cl}\phantom{..}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\end{array}\]
The structures of six organic compounds are shown:
|
A \[\begin{array}{cc} |
B \[\begin{array}{cc} |
C \[\begin{array}{cc} |
|
D \[\begin{array}{cc} |
E \[\begin{array}{cc} |
F \[\begin{array}{cc} |
- Identify two of the compounds that are members of the same homologous series but are not isomers.
- Which two compounds are isomers of each other?
- F can be prepared from D. Give a chemical equation for the reaction.
