Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given below are the F2 – phenotypic ratios of two independently carried monohybrid crosses :
(i) 1 : 2 : 1
(ii) 3 : 1
Mention what does each ratio suggest.
उत्तर
(i) 1 : 2 : 1 - Phenotypic ratio
Suggest that the phenomenon is incomplete dominance
* When neither of the alleles of a character is completely dominant over the other and the F1 hybrid is intermediate between the two parents, the phenomenon is Incomplete dominance.
* The phenotypic and genotypic ratio in F2 generation is 1:2:1 in this case.
(ii) 3:1 - Phenotypic ratio
Suggest that the phenomena has monohybrid cross. Monohybrid cross is a cross which involves only a single pair of contrasting characters. The parental generation has genotype for pure gene which on cross produces homozygous progeny i.e. F1 generation. On selfing F1 generation obtain F2 generation. The F2 generation has phenotypic ratio 3 : 1.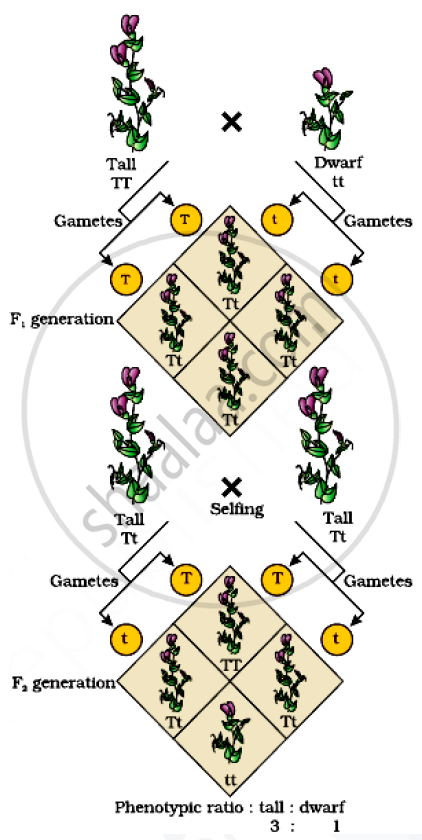
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Differentiate between the following -
Homozygous and Heterozygous
Differentiate between the following -
Monohybrid and Dihybrid.
Pure-bred tall pea plants are first crossed with pure-bred dwarf pea plants. The pea plants obtained in the F1 generation are then selfed to produce F2 generation of pea plants.
Which type of plants was missing in the F1 generation but reappeared in the F2 generation?
Give reasons why acquired characters are not inherited.
Genotypic ratio of a monohybrid cross is ______.
A Monohybrid cross is ______
Cross between hybrid and recessive parent:
In a plant tallness is dominant over dwarfness and red flower is dominant over white. Starting with the parents work out a dihybrid cross. What is standard dihybrid ratio? Do you think the values would deviate if the two genes in question are interacting with each other?
Assertion (A): In humans, if gene (B) is responsible for black eyes and gene (b) responsible for brown eyes, then the colour of eyes of the progeny having gene combination Bb, bb or BB will be black only.
Reason (R): The black colour of the eyes is a dominant trait.
