Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
Monohybrid cross is one where the parents used for hybridization differ in only one pair of contrasting characters or alleles.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A child has blood group O. If the father has blood group A and mother blood group B, work out the genotypes of the parents and the possible genotypes of the other offsprings.
Given below are the F2 – phenotypic ratios of two independently carried monohybrid crosses :
(i) 1 : 2 : 1
(ii) 3 : 1
Mention what does each ratio suggest.
A certain couple got four daughters in a sequence and no son. Does it mean that the husband does not produce Y-chromosome bearing sperms? Explain. What is the chance of this couple having a daughter?
A garden pea plant produces axial white flowers. Another of the same species produced terminal violet flowers. Identify the dominant trait?
What do you understand by the terms phenotype and genotype?
A pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with the pure dwarf plant (tt), what would be the F1 and F2 generations? Explain.
Pure-bred tall pea plants are first crossed with pure-bred dwarf pea plants. The pea plants obtained in the F1 generation are then selfed to produce F2 generation of pea plants.
Which type of plants was missing in the F1 generation but reappeared in the F2 generation?
A Monohybrid cross is ______
In a monohybrid cross of plants with red and white flowered plants, Mendel got only red-flowered plants. On self-pollinating these F1 plants got both red and white flowered plants in 3:1 ratio. Explain the basis of using RR and rr symbols to represent the genotype of plants of parental generation.
Given below is a schematic representation of the inheritance of the shape of the seeds of garden peas. Answer the questions that follow:
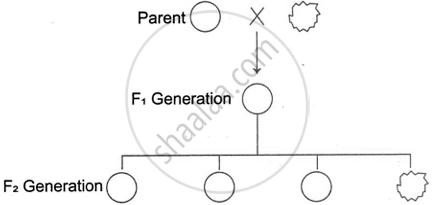
- Which is the dominant and recessive allele of the trait?
- What does the ratio 3 : 1 in the F2 generation represent?
- State Mendel's Law of Dominance.
