Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given below is a schematic representation of the inheritance of the shape of the seeds of garden peas. Answer the questions that follow:
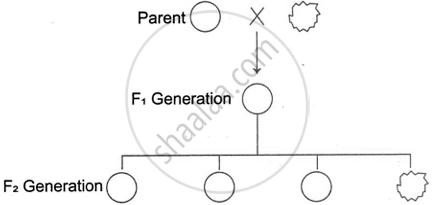
- Which is the dominant and recessive allele of the trait?
- What does the ratio 3 : 1 in the F2 generation represent?
- State Mendel's Law of Dominance.
उत्तर
- The dominant allele is R (for round seeds), while the recessive allele is r (for wrinkled seeds). This is obvious because only round seeds develop in F1, whereas the wrinkled characteristic is entirely concealed.
- 3:1 indicates that three of the four seeds are spherical and one is wrinkled. That is, 75% of the F2 progeny have round seeds (the dominant characteristic), but only 25% have wrinkled seeds (the recessive trait).
- Mendel's law of dominance states that if an organism has two distinct alleles for a trait, the dominant allele will be expressed, hiding the recessive allele. This means that only the dominant allele determines the organism's phenotype.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Differentiate between the following -
Homozygous and Heterozygous
Differentiate between the following -
Monohybrid and Dihybrid.
A child has blood group O. If the father has blood group A and mother blood group B, work out the genotypes of the parents and the possible genotypes of the other offsprings.
A garden pea plant produces axial white flowers. Another of the same species produced terminal violet flowers. Identify the dominant trait?
Pure-bred tall pea plants are first crossed with pure-bred dwarf pea plants. The pea plants obtained in the F1 generation are then selfed to produce F2 generation of pea plants.
What is the ratio of tall plants to dwarf plants in the F2 generation?
Differentiate between inherited and acquired characters. Give one example for each type.
Genotypic ratio of a monohybrid cross is ______.
Cross between hybrid and recessive parent:
