Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Good Y is a substitute of good X. The price of Y falls. Explain the chain of effects of this change in the market of X.
उत्तर
Substitute goods refer to goods which can be consumed instead of each other. For example, tea and coffee are substitute goods. In case of substitute goods, the demand for a good share a positive relation with the price of the substitute good.
Fall in price of substitute good Y: With a fall in the price of the substitute good Y, the demand of the concerned good falls. For example, with a fall in the price of coffee, the demand for tea increases.
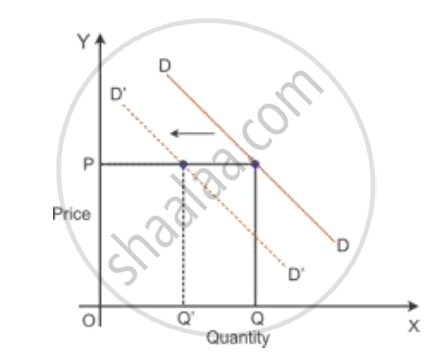
According to the diagram, DD is the initial demand curve for good X. At price OP, OQ quantity of good X is demanded. With a fall in the price of good Y, the demand for good X falls. Accordingly, the demand curve for good X shifts parallelly leftwards to D′D′. Here, even at the existing price OP, the quantity demand of good X falls to OQ′.
संबंधित प्रश्न
When does ‘increase’ in demand take place?
Explain the effect of change in prices of the related goods on demand for the given good.
Explain how do the following influence demand for a good:
i. Rise in income of the consumer.
ii. Fall in prices of the related goods
Distinguish between individuals demand and market demand.
If with the rise in the price of good Y, demand for good X rises, the two goods are: (Choose the correct alternative)
a. Substitutes
b. Complements
c. Not related
d. Jointly demanded
How does change in the price of a substitute good affect the demand of the given good? Explain with the help of an example.
Fill in the blank using proper alternative given in the bracket:
Market demand is a total demand of...............buyers.
Do you agree with the following statement? Give reason
State and explain the law of demand.
Statements related to decrease in demand
- It is a type of change in demand
- It takes place due to unfavourable changes in other factors like tastes, income etc.
- Price remains constant
- Demand curve shifts to the right hand side of the original demand curve
Assertion (A): Under exceptional cases, demand curve has a positive slope.
Reasoning (R): In exceptional cases, consumer buys more when the price of a commodity rises and buys less when the price of commodity falls.
The shape of supply curve is ______
Identify the correctly matched items from Column I to that of Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (1) Demand Curve of Perfect Competition | (a) V-shaped Curve |
| (2) Demand Curve of Monopoly | (b) U-shaped Curve |
| (3) Demand Curve of Monopolistic Competition | (c) Upward rising |
| (4) Demand Curve of Oligopoly | (d) In-determinant |
In case of perfect competition, AR curve is:
Explain why the demand curve slopes downwards.
- Assertion (A): The demand curve slopes downwards.
- Reasoning (R): A fall in the price of goods increases the real income of the consumer enabling him/her to buy more.
Study the following table and answer the questions:
| Price of Ice Cream (₹) | Quantity Supplied | Market Supply | ||
| Seller A | Seller B | Seller C | (A + B + C) | |
| 50 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 7 |
| 100 | 1 | `square` | 10 | 15 |
| 150 | `square` | 6 | 15 | 23 |
| 200 | 3 | 8 | 20 | `square` |
| 250 | 4 | 10 | `square` | 39 |
Questions:
- Complete the above table.
- State whether the following statements are True or False.
(a) Market supply has a direct relation to price.
(b) As the price rises from ₹50 to ₹250, market supply rises from 7 to 39. This indicates an increase in supply.
Study the following diagram and answer the questions:
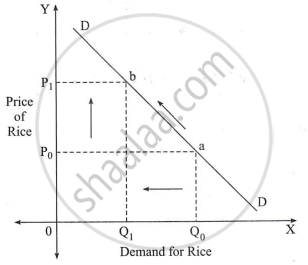
Questions:
- In which direction does the demand curve slope?
- What is the reason for the fall in demand of rice from Q0 to Q1?
Draw a straight-line demand curve joining both the axes. Indicate the following on the demand curve.
Elasticity of demand is equal to zero
