Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A current i1 = i0 sin ωt passes through a resistor of resistance R. How much thermal energy is produced in one time period? A current i2 = −i0 sin ωt passes through the resistor. How much thermal energy is produced in one time period? If i1 and i2 both pass through the resistor simultaneously, how much thermal energy is produced? Is the principle of superposition obeyed in this case?
उत्तर
The thermal energy produced for an AC circuit in one time period is given by,
H = `Irms^2xx R xx (2pi)/omega`
For current, i1 = i0 sin ωt,
⇒ H = `(i_0^2R)/2 xx (2pi)/omega = (pii_0^2R)/omega`
For current, i2 = −i0 sin ωt,
`Irms = i_0/sqrt(2)`
Hence, the same thermal energy will be produced due to this current.
Since, the direction of i1 and i2 are opposite and their magnitude is same, the net current through the resistor will become zero when both are passed together. Yes, the principle of superposition is obeyed in this case.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the current leads the voltage in phase by π/2 in an AC circuit containing an ideal capacitor ?
When an AC source is connected to a capacitor, there is a steady-state current in the circuit. Does it mean that the charges jump from one plate to the other to complete the circuit?
Is energy produced when a transformer steps up the voltage?
A transformer is designed to convert an AC voltage of 220 V to an AC voltage of 12 V. If the input terminals are connected to a DC voltage of 220 V, the transformer usually burns. Explain.
The AC voltage across a resistance can be measured using
The dielectric strength of air is 3.0 × 106 V/m. A parallel-plate air-capacitor has area 20 cm2 and plate separation 0.10 mm. Find the maximum rms voltage of an AC source that can be safely connected to this capacitor.
A transformer has 50 turns in the primary and 100 in the secondary. If the primary is connected to a 220 V DC supply, what will be the voltage across the secondary?
If circuit containing capacitance only, the current ______.
A.C. power is transmitted from a power house at a high voltage as ______.
When an ac voltage of 220 V is applied to the capacitor C, then ______.
When an AC voltage of 220 V is applied to the capacitor C ______.
- the maximum voltage between plates is 220 V.
- the current is in phase with the applied voltage.
- the charge on the plates is in phase with the applied voltage.
- power delivered to the capacitor is zero.
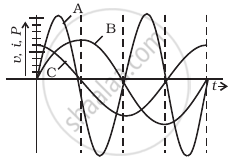
A device ‘X’ is connected to an a.c source. The variation of voltage, current and power in one complete cycle is shown in figure.
- Which curve shows power consumption over a full cycle?
- What is the average power consumption over a cycle?
- Identify the device ‘X’.
Explain why the reactance provided by a capacitor to an alternating current decreases with increasing frequency.
Define Capacitive reactance.
