Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How are polysaccharides and disaccharides digested?
उत्तर
The digestion of carbohydrates takes place in the mouth and the small intestine region of the alimentary canal. The enzymes that act on carbohydrates are collectively known as carbohydrases.
Digestion in the mouth:
As food enters the mouth, it gets mixed with saliva. Saliva – secreted by the salivary glands – contains a digestive enzyme called salivary amylase. This enzyme breaks down starch into sugar at pH 6.8.
Starch  Maltose + Isomaltose + Limit dextrins
Maltose + Isomaltose + Limit dextrins
Salivary amylase continues to act in the oesophagus, but its action stops in the stomach as the contents become acidic. Hence, carbohydrate-digestion stops in the stomach.
Digestion in the small intestine:
Carbohydrate-digestion is resumed in the small intestine. Here, the food gets mixed with the pancreatic juice and the intestinal juice. Pancreatic juice contains the pancreatic amylase that hydrolyses the polysaccharides into disaccharides.
Starch  Disaccharides
Disaccharides
(Polysaccharides)
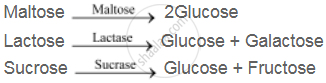
Similarly, the intestinal juice contains a variety of enzymes (disaccharidases such as maltase, lactase, sucrase, etc.). These disaccharidases help in the digestion of disaccharides. The digestion of carbohydrates is completed in the small intestine.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the correct answer among the following:
Succus entericus is the name given to
(i) a junction between ileum and large intestine
(ii) intestinal juice
(iii) swelling in the gut
(iv) appendix
Match column I with column II
| Column I | Column II | ||
| a | Bilirubin and biliverdin | 1 | Parotid |
| b | Hydrolysis of starch | 2 | Bile |
| c | Digestion of fat | 3 | Lipases |
| d | Salivary gland | 4 | Amylases |
How does pepsinogen change into its active form?
Answer briefly:
How does bile help in the digestion of fats?
Describe the process of digestion of protein in stomach.
Bile juice contains no digestive enzymes, yet it is important for digestion. Why?
Mark the right statement among the following
Trypsinogen is an inactive enzyme of pancreatic juice. An enzyme, enterokinase, activates it. Which tissue/ cells secrete this enzyme?/ How is it activated?
Name the enzymes involved in the breakdown of nucleotides into sugars and bases?
Define digestion in one sentence.
Correct the following statement by deleting one of entries (given in bold).
Goblet cells are located in the intestinal mucosal epithelium and secrete chymotrypsin/mucus.
Correct the following statement by deleting one of entries (given in bold).
Fats are broken down into di- and monoglycerides with the help of amylase/ lipases.
Correct the following statement by deleting one of entries (given in bold).
Saliva contains enzymes that digest starch/protein.
Name the part of the alimentary canal where major absorption of digested food takes place. What are the absorbed forms of different kinds of food materials?
Correct the statement given below by the right option shown in the bracket against them.
Rennin is a proteolytic enzyme found in gastric juice in (infants/adults).
Correct the statement given below by the right option shown in the bracket against them.
Dipeptides, disaccharides and glycerides are broken down into simple substances in region of small intestine. (jejunum/duodenum)
How is the intestinal mucosa protected from the acidic food entering from stomach?
Describe the enzymatic action on fats in the duodenum.
