Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How did an American Company, Eli Lilly use the knowledge of r-DNA technology to produce human insulin?
उत्तर
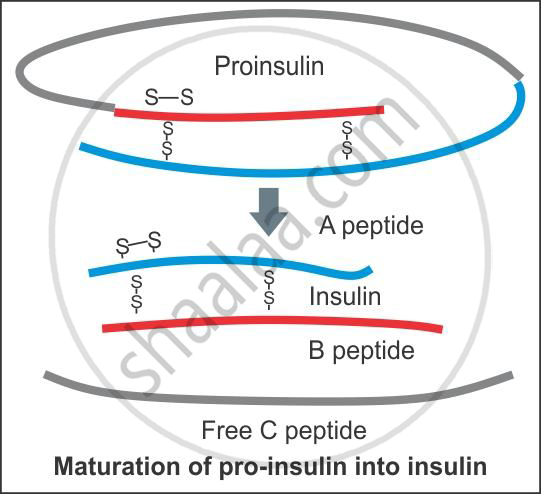
The structure of insulin consists of two short polypeptide chains—chain A and chain B—linked together by disulphide bridges. In mammals, including human beings, insulin is synthesised as a pro-hormone which contains an extra stretch called the C peptide which is removed during maturation into insulin. The rDNA technique is used for assembling insulin into the mature form.
In 1983, Eli Lily, an American company, prepared two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B chains of human insulin and introduced them in the plasmids of E. coli to produce insulin chains. Chains A and B were produced separately, extracted and combined by creating disulphide bonds to form human insulin.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain enzyme – replacement therapy to treat adenosine deaminase deficiency. Mention two disadvantages of this procedure.
Recombination DNA−technology is of great importance in the field of medicine. With the help of a flow chart, show how this technology has been used in preparing genetically engineered human insulins.
Expand the Given and mention one application of each:
ELISA
Write any two biochemical/molecular diagonostic procedures for early detection of viral infection. Explain the principle of any one of them.
If a person thinks he is infected with HIV, due to unprotected sex, and goes for a blood test. Do you think a test such as ELISA will help? If so why? If not, why?
Which is false about antibiotics?
For effective treatment of the disease, early diagnosis and understanding of its pathophysiology is very important. Which of the following molecular diagnostic techniques is very useful for early detection?
Can a disease be detected before its symptoms appear? Explain the principle involved.
What is a recombinant DNA vaccine? Give two examples.
Name the technique used to detect the presence of HIV in the body of an individual, Justify the principle associated with this technique.
