Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How did Hershey and Chase differentiate between DNA and protein in their experiment while proving that DNA is the genetic material?
उत्तर
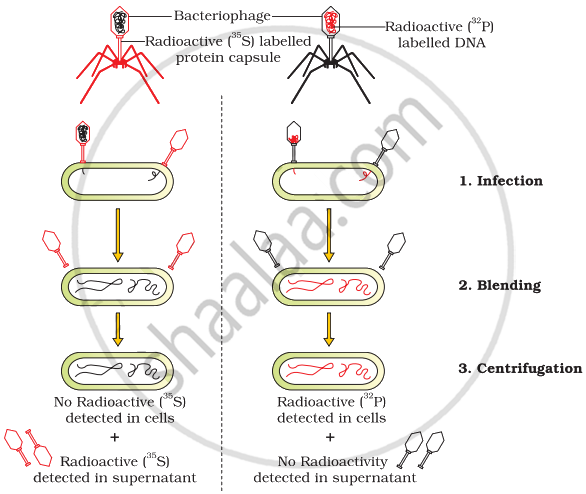
Hershey and Chase, in order to prove DNA as genetic material, cultured E. coli bacteria in medium containing P32 and P32 isotopes. After growing for some time, the bacteria were infected by bacteriophage. After infection, it was observed that the protein coat of bacteriophage had become radioactive with S35 whereas its DNA does not contain sulphur. On the contrary, the DNA of the bacteriophage was showing the presence of P32 radioactive isotopes because DNA contains phosphorus. P32 was absent in the protein coat. Bacteriophage containing P32 radioactive elements was infected with such bacteria which did not contain radioactive elements. After infection, it was observed that all the bacteria had become radioactive. Most of the radioactive isotopes were also transferred to the next generation of bacteriophage.
On infecting bacteria devoid of radioactive elements with bacteriophage containing S32 and then separating the bacteriophage, it was observed that radioactive elements were not present in the bacteria but these remained in the protein envelope of the bacteriophage. The above experiment proves that the DNA of the bacteriophage is the substance which produces new bacteriophages and takes part in infection. It has been proved that DNA is the genetic material and not protein. Besides this, DNA contains phosphorus whereas protein does not contain phosphorus. DNA is devoid of sulphur whereas protein contains sulphur.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Enlist types of DNA library.
Many copies of a specific gene of interest are required to study the detailed sequencing of bases in it. Name and explain the process that can help in developing large number of copies of this gene of interest.
Describe the experiment of Hershey and Chase to prove that DNA is the genetic material.

Hershey and Chase Experiment
Give a reason why :
DNA cannot pass into a host cell through the cell membrane.
Multiple Choice Question:
Griffith worked on ____________.
Explain Avery, McCarty, and MacLeod’s experiment in detail.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram explaining Meselson’s and Stahl’s experiment.
Identify the observations that were made in Hershey-Chase's experiment, when the radioactive viruses were allowed to infect E. coli.
P. E. coli which were infected by viruses with radioactive DNA became radioactive.
Q. E. coli which were infected by viruses with radioactive protein did not become radioactive.
R. E. coli which were infected by viruses with radioactive protein became radioactive.
S. E. coli which were infected by viruses with radioactive DNA did not become radioactive.
When DNA is transferred from a culture of capsulated Streptococcus to a culture of non-capsulated Streptococcus, converting the latter into the former type, the process is known as ____________.
Who among the following discovered transformation?
Identify the component common to both DNA and RNA.
Which of the following was used by Hershey and Chase to provide the unambiguous proof that DNA is the genetic material?
What would happen if we inject a mice with the mixture of heat killed S-type and living R-type?
Identify the conclusion drawn by Griffith from his experiments.
Study the following statements and select the correct option.
- 'R' strain of S. pneumoniae is nonvirulent, rough, non-pathogenic, and non-capsulated.
- 'S' strain of S pneumoniae is virulent, smooth, pathogenic, and encapsulated.
Hershey and Chase proved that genetic material is DNA, by using the organism ______
Name the conjugated protein used as genetic material in living cells.
Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod, and Maclyn McCarty used enzymes to purify biochemicals such as proteins, DNA, and RNA from the heat-killed S cells to see which ones could transform live R cells into S cells in Griffith's experiment. They observed that ______
Name the scientist who experimentally demonstrated that "DNA is the genetic material."
Nucleic acids are the infective substances in viruses were discovered by:
