Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How does the speed of light determine the optical density of a medium?
उत्तर १
If the speed of light in a medium is less than the speed of light in air, means the MEDIUM is DENSER than air.
If the speed of light is more than the speed of light in AIR, means the MEDIUM is LESS DENSER than air.
Speed of light is 1/density of medium
उत्तर २
- Definition of Optical Density: Optical density refers to how much a medium can slow down the speed of light compared to its speed in a vacuum.
- Speed of Light in Different Media: Light travels fastest in a vacuum (c = 3 × 108 m/s). When light enters a medium (like water, glass, or air), its speed decreases depending on the medium's optical density.
- Relation Between Speed and Optical Density: The greater the optical density, the slower the speed of light in the medium. For example, light travels more slowly in glass than in air because glass has a higher optical density.
- Refractive Index: The optical density is quantified using the refractive index (n), which is defined as: `n = c/v`
- Example:
- In air: n ≈ 1, light speed is almost the same as in a vacuum.
- In water: n ≈ 1.33, light slows down significantly.
- In glass: n ≈ 1.5, light slows down even more.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Describe an activity to show that colours of white light splitted by a glass prism can be recombined to get white light by another identical glass prism. Also draw ray diagram to show the recombination of the spectrum of white light.
What is spectrum? What is the name of glass shape used to produce a spectrum?
A ray of white light falls on a prism. Draw a ray diagram to show that the prism disperses the white light.
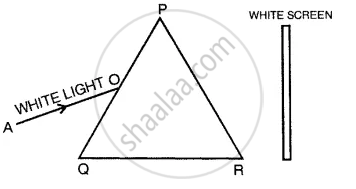
In figure AO is the ray of white light falling on a prism PQR. Complete the diagram till the light emerges out from the prism and falls on the screen.
You are given a disc divided into seven sectors with colours violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red in them. What would be its colour when it is rotated rapidly?
In an experiment to trace the path of a ray of light through a triangular glass prism, a student would observe that the emergent ray
(a) is parallel to the incident ray.
(b) is along the same direction of incident ray.
(c) gets deviated and bends towards the thinner part of the prism.
(d) gets deviated and bends towards the thicker part (base) of the prism.
Draw a labelled diagram: Dispersion of light through a prism.
What is the cause of the dispersion of white light through a glass prism? Draw a ray diagram to show the path of light when two identical glass prisms are arranged together in an inverted position with respect to each other and a narrow beam of white light is allowed to fall obliquely on one of the faces of the prisms.
Suggest one way, in each case, by which we can detect the presence of Infrared radiations.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram for dispersion of light.
