Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A uniform meter scale is in equilibrium as shown in the diagram :
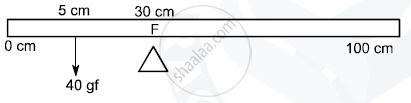
(i) Calculate the weight of the meter scale.
(ii) Which of the following options is correct to keep the ruler in equilibrium when 40 gf wt is shifted to 0 cm mark ?
F is shifted towards 0 cm
or
F is shifted towards 100 cm
उत्तर

(i) Mass of the meter scale wiil be concentrated at its centre
∴ At 50 cm, Mass of meter scale = M gf
`therefore F_1d_1= F_2 d_2`
`(25) = F_2(20)`
50 gf = F2
0.49N = F2
∴ F2 = m (9.8)
`=(0.49)/(9.8)= m`
∴ m = 0.05kg
1m = 500m
(ii) F is shifted towards 0 cm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the condition when a body is in dynamic equilibrium.
State the principle of moments. Give one device as an application of it
State the principle of moments. A meter scale is pivoted at 30 cm mark and it is in equilibrium when a mass of 40 g is suspended from 10 cm mark. Calculate the mass of the ruler.
What makes a balance faulty?
In equilibrium algebraic sum of moments of all forces about the point of rotation is ______.
In figure, a uniform bar of length l m is supported at its ends and loaded by a weight W kgf at its middle. In equilibrium, find the reactions R1 and R2 at the ends.
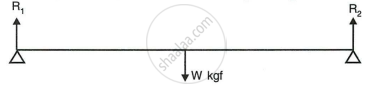
`["Hint:" "In equilibrium" "R"_1 + "R"_2 = "W" "and" "R"_1 xx l/2 = "R"_2 xx l/2]`
Explain why It is easier to knock down a boy who is standing on one foot than one who is standing on two.
Mention any two conditions for the stability of a body?
Give one example of static equilibrium.
