Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In figure, a uniform bar of length l m is supported at its ends and loaded by a weight W kgf at its middle. In equilibrium, find the reactions R1 and R2 at the ends.
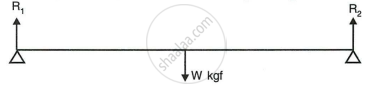
`["Hint:" "In equilibrium" "R"_1 + "R"_2 = "W" "and" "R"_1 xx l/2 = "R"_2 xx l/2]`
उत्तर
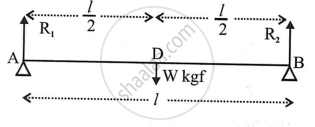
As D is the mid-point of AB `(l)`
∴ AD = DB = `l/2`
The usual responses R1 and R2, which act upward, balance the bar's weight W, which acts downward toward the center of the earth.
∴In equilibrium, R1 + R2 = W
Total upward reaction = (R1 × AD) + (R2 × DB)
= `(R_1 xx l/2) + (R_2 xx l/2)`
∵ `R_1 xx l/2 + R_2 xx l/2 = R` ...(suppose)
Total upward reaction = downward wt. of bar.
∴ R + R = W
2R = W
R = `"W"/2`
∴ R1 = `"W"/2 " kgf"` and R2 = `"W"/2 " kgf"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the principle of moments. Give one device as an application of it
State two conditions for a body acted upon by several forces to be in equilibrium.
A faulty balance of unequal arms and pans of unequal weights is used to find the true weight of a metal. By double weighing the weights are found to be 1210 g and 1000 g. Calculate the true weight of the metal.
Explain why It is easier to knock down a boy who is standing on one foot than one who is standing on two.
What is the weight of a body placed at the centre of the earth?
What do you mean by dynamic and static equilibrium? Give one example of each.
A boy of mass 30 kg is fitting at a distance of 2 m from the middle of a see-saw. Where should a boy of mass 40 kg sit so as to balance the see-saw?
A ball is placed on a compressed spring. When the spring is released, the ball is observed to fly away.
(i) What form of energy does the compressed spring possess?
(ii) Why does the ball fly away?
Explain the types of stability with suitable examples.
Mention any two conditions for the stability of a body?
