Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In figure, a uniform bar of length l m is supported at its ends and loaded by a weight W kgf at its middle. In equilibrium, find the reactions R1 and R2 at the ends.
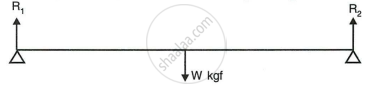
`["Hint:" "In equilibrium" "R"_1 + "R"_2 = "W" "and" "R"_1 xx l/2 = "R"_2 xx l/2]`
उत्तर
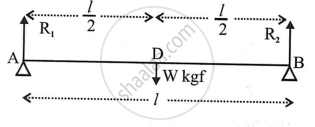
As D is the mid-point of AB `(l)`
∴ AD = DB = `l/2`
The usual responses R1 and R2, which act upward, balance the bar's weight W, which acts downward toward the center of the earth.
∴In equilibrium, R1 + R2 = W
Total upward reaction = (R1 × AD) + (R2 × DB)
= `(R_1 xx l/2) + (R_2 xx l/2)`
∵ `R_1 xx l/2 + R_2 xx l/2 = R` ...(suppose)
Total upward reaction = downward wt. of bar.
∴ R + R = W
2R = W
R = `"W"/2`
∴ R1 = `"W"/2 " kgf"` and R2 = `"W"/2 " kgf"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define equilibrium.
State the condition when a body is in static equilibrium.
A uniform meter scale is in equilibrium as shown in the diagram :
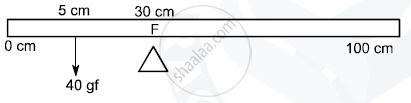
(i) Calculate the weight of the meter scale.
(ii) Which of the following options is correct to keep the ruler in equilibrium when 40 gf wt is shifted to 0 cm mark ?
F is shifted towards 0 cm
or
F is shifted towards 100 cm
State the principle of moments. A meter scale is pivoted at 30 cm mark and it is in equilibrium when a mass of 40 g is suspended from 10 cm mark. Calculate the mass of the ruler.
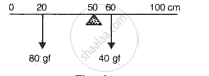
The arms of a beam balance are 20 cm and 21 cm, but the pans are of equal weight. By the method of double weighing the weights are found to be 1000 g and 20 g. Find the actual weight of the body
A faulty balance of unequal arms and pans of unequal weights is used to find the true weight of a metal. By double weighing the weights are found to be 1210 g and 1000 g. Calculate the true weight of the metal.
Define the term momentum.
State two conditions when the work done by a force acting on a body is zero.
Explain the concept which is used in the continuous movement of the Thanjavur doll?
Give one example of static equilibrium.
