Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If `bara and barb` are any two non-zero and non-collinear vectors then prove that any vector `barr` coplanar with `bara` and `barb` can be uniquely expressed as `barr = t_1bara + t_2barb` , where t1 and t2 are scalars.
उत्तर
Let `bara, barb, barr` be coplanar.
Take any point O in the plane of `bara, barb` and `barr`.
Represents the vectors `bara, barb` and `barr` by `bar(OA), bar(OB)` and `bar(OR)`.
Take the point P on `bara` and Q on `barb` such that OPRQ is a parallelogram.
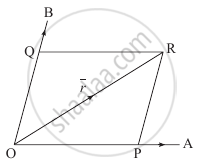
Now, `bar(OP)` and `bar(OA)` are collinear vectors.
∴ There exists a non-zero scalar t1 such that
`bar(OP) = t_1 * bar(OA) = t_1 * bara`
Also, `bar(OQ)` and `bar(OB)` are collinear vectors.
∴ There exists a non-zero scalar t2 such that
`bar(OP) = t_2 * bar(OB) = t_2 * barb`
Now, by parallelogram law of addition of vectors,
`bar(OR) = bar(OP) + bar(OQ)`
∴ `barr = t_1bara + t_2barb`
Thus, `barr` is expressed as a linear combination `t_1bara + t_2barb`.
Uniqueness: Let, if possible,
`barr = t_1^'bara + t_2^'barb`, where t1', t2' are non-zero scalars.
Then, `t_1bara + t_2barb = t_1^'bara + t_2^'barb`
∴ `(t_1 - t_1^')bara = -(t_2 - t_2^')barb` .....(1)
We want to show that t1 = t1' and t2 = t2'
Suppose t1 ≠ t1', i.e. t1 – t1' ≠ 0 and t2 ≠ t2, i.e. t2 – t2 ≠ 0
Then dividing both sides of (1) by t1 – t1', we get
`bara = -((t_2 - t_2^')/(t_1 - t_1^'))barb`
This shows that the vector `bara` is a non-zero scalar multiple of `barb`.
∴ `bara` and `barb` are collinear vectors.
This is a contradiction, since `bara, barb` are given to be non-collinear.
∴ t1 = t1'
Similarly, we can show that t2 = t2'
This shows that `barr` is uniquely expressed as a linear combination `t_1bara + t_2barb`.
Conversely: Let `barr = t_1bara + t_2barb`, where t1, t2 are scalars.
Since `bara, barb` are coplanar, `t_1bara, t_2barb` are also coplanar.
∴ `barr = t_1bara + t_2barb` is coplanar with `bara` and `barb`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If `|bar("a")|` = 2, `|bar("b")|` = 5, and `bar("a")*bar("b")` = 8 then `|bar("a") - bar("b")|` = ______
Represent graphically the displacement of 45 cm, 30° north of east
Represent graphically the displacement of 80 km, 60° south of west
If `(bar"a" + 2bar"b" - bar"c") * [(bar"a" - bar"b") xx (bar"a" - bar"b" - bar"c")] = "k"[bar"a" bar"b" bar"c"]`, then the value of k is
A line makes angles α, β, γ with the co-ordinate axes and α + β = 90°, then γ = ______.
The angle between two adjacent sides `overlinea` and `overlineb` of parallelogram is `pi/6`. if `overlinea` = (2, -2, 1) and `|overlineb| = 2|overlinea|`, then area of this parallelogram is ______
If C is the midpoint of AB and P is any point outside AB, then ______
Which of the following is not equal to w · (u × v)?
If `overline (a) =10hat("i") + lambda hat("j") + 2hat("k")` is perpendicular to `overline (b)= hat ("i")+hat("j")-hat("k")`, then λ is equal to ______.
The position vectors of three consecutive vertices of a parallelogram are `hat"i" + hat"j" + hat"k", hat"i" + 3hat"j" + 5hat"k"` and `7hat"i" + 9hat"j" + 11hat"k"`. Find the position vector of the fourth vertex.
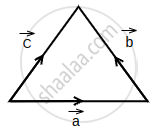
If `veca + vecb = vecc ((λx)hati + yhatj + 4zhatk) + (yhati + xhatj + 3yhatk) = -zhati - 2zhatj - (λ + 1)xhatk` are sides of triangle as shown is figure then value of λ is ______.
(where x, y, z are not all zero)
If a = `veca = hati + hatj - 2hatk, vecb = 2hati - hatj + hatk` and `vecc = 3hati - hatk` and `vecc = mveca + nvecb`, then m + n is equal to ______.
Let a = `hati + 2hatj + hatk`, b = `hati - hatj + hatk`, c = `hati + hatj - hatk`. A vector coplanar to a and b has a projection along with c of magnitude `1/sqrt(3)`, then the vector is ______.
If a, b and c are three non-zero vectors which are pairwise non-collinear. If a + 3b is collinear with c and b + 2c is collinear with a, then a + 3b + 6c is ______.
The position vectors of vertices of ΔABC are `4hati - 2hatj; hati + 4hatj - 3hatk` and `-hati + 5hatj + hatk` respectively, then ∠ABC = ______.
If a = `3hati - 2hatj + hatk` and b = `2hati - 4hatj - 3hatk`, then | a – 2b | will be ______.
In the triangle PQR, `bar("PQ") = 2bar "a"` and `bar("QR") = 2bar "b".` The mid-point of PR is M. Find the following vectors in terms of `bar "a" "and" bar"b"`.
In the triangle PQR, `\overline"PQ"` = 2`\overline"a"` and `\overline"QR"` = 2`\overline"b"`. The mid-point of PR is M. Find the following vectors in terms of `\overline"a"` and `\overline "b"`.
- `\overline"PR"`
- `\overline"PM"`
- `\overline"QM"`
Check whether the vectors `2hati + 2hatj + 3hatk, -3hati + 3hatj + 2hatk, "and" 3hati + 4hatk` form a triangle or not.
In the triangle PQR, `bar(PQ)` = 2 `bara` and `bar(QR)` = 2 `barb`. The mid-point of PR is M. Find the following vectors in terms of `bara` and `barb`.
- `bar(PR)`
- `bar(PM)`
- `bar(QM)`
Check whether the vectors `2 hati+2hatj+3hatk-3hati+3hatj+2hatk and 3hati+4hatk`form a triangle or not.
