Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If a constant potential difference is applied across a bulb, the current slightly decreases as time passes and then becomes constant. Explain.
उत्तर
As a constant potential difference is applied across a bulb, due to Joule's heating effect, the temperature of the bulb increases. As the temperature of the bulb filament increases, its resistance also increases, as resistance R is the function of temperature T. It is given by R = R0(1+αT). With an increase in the value of resistance, the value of current decreases as \[i = \frac{V}{R}.\] Now, the heat generated by the resistance is constantly radiated to the surroundings. Thus, the value of its temperature is maintained and hence its resistance. As a result, current through the bulb filament becomes constant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
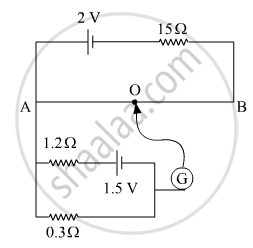
In the following potentiometer circuit, AB is a uniform wire of length 1 m and resistance 10 Ω. Calculate the potential gradient along the wire and balance length AO (= l).
Describe the working principle of a solar cell. Mention three basic processes involved in the generation of emf.
Why is potentiometer preferred over a voltmeter for comparison of emf. of cells?
The emf of a cell is always greater than its terminal voltage. Why? Give reason.
Identify the correct options.
(a) An ammeter should have small resistance.
(b) An ammeter should have large resistance.
(c) A voltmeter should have small resistance.
(d) A voltmeter should have large resistance.
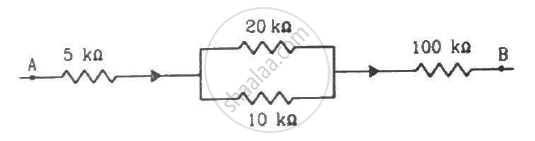
The following figure shows a part of a circuit. If a current of 12 mA exists in the 5 kΩ resistor, find the currents in the other three resistors. What is the potential difference between the points A and B?
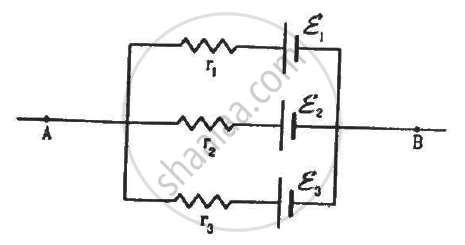
In the circuit shown in the figure, ε1 = 3 V, ε2 = 2 V, εa = 1 V and r1 = r2 = r3 = 1Ω. Find the potential difference between the points A and B and the current through each branch.
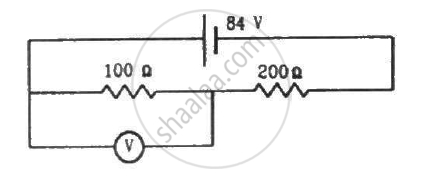
A voltmeter of resistance 400 Ω is used to measure the potential difference across the 100 Ω resistor in the circuit shown in the figure. (a) What will be the reading of the voltmeter? (b) What was the potential difference across 100 Ω before the voltmeter was connected?
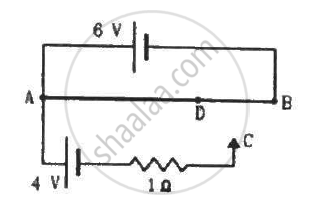
A 6-volt battery of negligible internal resistance is connected across a uniform wire AB of length 100 cm. The positive terminal of another battery of emf 4 V and internal resistance 1 Ω is joined to the point A, as shown in the figure. Take the potential at B to be zero. (a) What are the potentials at the points A and C? (b) At which point D of the wire AB, the potential is equal to the potential at C? (c) If the points C and D are connected by a wire, what will be the current through it? (d) If the 4 V battery is replaced by a 7.5 V battery, what would be the answers of parts (a) and (b)?
A copper strip AB and an iron strip AC are joined at A. The junction A is maintained at 0°C and the free ends B and C are maintained at 100°C. There is a potential difference between _______________ .
(a) the two ends of the copper strip
(b) the copper end and the iron end at the junction
(c) the two ends of the iron strip
(d) the free ends B and C
The potential difference across the terminals of a battery of emf 12 V and internal resistance 2 Ω drops to 10 V when it is connected to a silver voltameter. Find the silver deposited at the cathode in half an hour. Atomic weight of silver is 107.9 g mol−1.
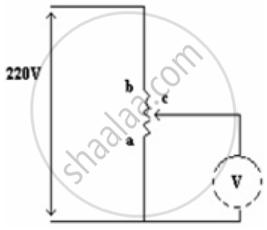
A potential difference of 220 V is maintained across 12000 Ω rheostat. Then voltmeter V has a resistance of 6000 Ω and point C is at one fourth the distance from a to b. Then the reading of voltmeter is ______.
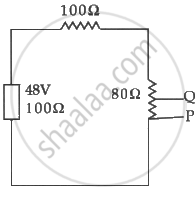
In the circuit in figure the potential difference across P and Q will be nearest to
The terminal potential difference of a cell is greater than its e.m.f when it is ______
