Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In Figure 1 below, a charge Q is fixed. Another charge q is moved along a circular arc MN of radius r around it, from the point M to the point N such that the length of the arc MN = l. The work done in this process is:
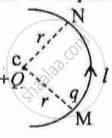
figure 1
विकल्प
zero
`1/(4piε_0).(Qq)/r^2l`
`(Qq)/(2ε_0r^2)l`
`(Qq)/(2piε_0r^2)`
उत्तर
In Figure 1 below, a charge Q is fixed. Another charge q is moved along a circular arc MN of radius r around it, from the point M to the point N such that the length of the arc MN = l. The work done in this process is: Zero
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Does the charge given to a metallic sphere depend on whether it is hollow or solid? Give reason for your answer.
Choose the correct option.
Two charges of 1.0 C each are placed one meter apart in free space. The force between them will be
Choose the correct option.
Two-point charges of A = +5.0 μC and B = -5.0 μC are separated by 5.0 cm. A point charge C = 1.0 μC is placed at 3.0 cm away from the centre on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the two point charges. The charge at C will experience a force directed towards
The number of lines of force that radiate outwards from one coulomb of charge is:-
A glass rod rubbed with silk is used to charge a gold-leaf electroscope and the leaves are observed to diverge. The electroscope thus charged is exposed to X-rays for a short period. Then ______
The dimensions of an atom are of the order of an Angstrom. Thus there must be large electric fields between the protons and electrons. Why, then is the electrostatic field inside a conductor zero?
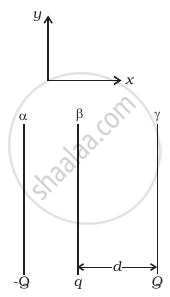
Two fixed, identical conducting plates (α and β), each of surface area S are charged to –Q and q, respectively, where Q > q > 0. A third identical plate (γ), free to move is located on the other side of the plate with charge q at a distance d (Figure). The third plate is released and collides with the plate β. Assume the collision is elastic and the time of collision is sufficient to redistribute charge amongst β and γ.
- Find the electric field acting on the plate γ before collision.
- Find the charges on β and γ after the collision.
- Find the velocity of the plate γ after the collision and at a distance d from the plate β.