Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
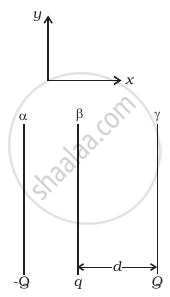
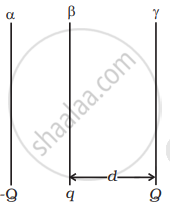
Two fixed, identical conducting plates (α and β), each of surface area S are charged to –Q and q, respectively, where Q > q > 0. A third identical plate (γ), free to move is located on the other side of the plate with charge q at a distance d (Figure). The third plate is released and collides with the plate β. Assume the collision is elastic and the time of collision is sufficient to redistribute charge amongst β and γ.
- Find the electric field acting on the plate γ before collision.
- Find the charges on β and γ after the collision.
- Find the velocity of the plate γ after the collision and at a distance d from the plate β.
उत्तर
a. The electric field at γ due to plate α is `- Q/(S2ε_0) hatx`
The electric field at γ due to plate β is `q/(S2ε_0) hatx`
Hence, the net electric field is E1 = `((Q - q))/(2ε_0S) (- hatx)`
b. During the collision plates β and γ are together and hence must be at one potential. Suppose the charge on β is q1 and on γ is q2. Consider a point O. The electric field here must be zero.
Electric field at 0 due to α = `- Q/(2ε_0S) hatx`
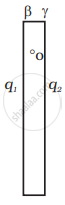
Electric field at 0 due to β = `q_1/(2ε_0S) hatx`
Electric field at 0 due to γ = `q_2/(2ε_0S) hatx`
∴ `(-(Q + q_2))/(2ε_0S) q_1/(2ε_0S)` = 0
⇒ q1 – q2 = Q
Further, q1 + q2 = Q + q
⇒ q1 = Q + q/2
And q2 = q/2
Thus the charge on β and γ are Q + q/2 and q/2, respectively.
c. Let the velocity be v at the distance d after the collision. If m is the mass of the plate γ, then the gain in K.E. over the round trip must be equal to the work done by the electric field. After the collision, the electric field at γ is
E2 = `- Q/(2ε_0S) hatx + ((Q + q/2))/(2ε_0S) hatx = (q/2)/(2ε_0S) hatx`
The work is done when the plate γ is released till the collision is F1d where F1 is the force on plate γ. The work done after the collision till it reaches d is F2d where F2 is the force on plate γ.
F1 = `E_1Q = ((Q - q)Q)/(2ε_0S)`
And F2 = `E_2 q/2 = (q/2)^2/(2ε_0S)`
∴ Total work done is `1/(2ε_0S) [(Q - q) Q + (q/2)^2]d = 1/(2ε_0S) (Q - q/2)^2d`
⇒ `(1/2)mv^2 = d/(2ε_0S) (Q - q/2)^2`
∴ `v = (Q - q/2)(d/(mε_0S))^(1/2)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the meaning of the statement ‘electric charge of a body is quantised’.
When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk cloth, charges appear on both. A similar phenomenon is observed with many other pairs of bodies. Explain how this observation is consistent with the law of conservation of charge.
In Figure 1 below, a charge Q is fixed. Another charge q is moved along a circular arc MN of radius r around it, from the point M to the point N such that the length of the arc MN = l. The work done in this process is:
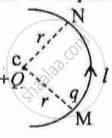
figure 1
Choose the correct option.
Two charges of 1.0 C each are placed one meter apart in free space. The force between them will be
Charge is quantized means ______.
The number of lines of force that radiate outwards from one coulomb of charge is:-
Eight dipoles of charge of magnitude ± e are placed inside a cube. The total electric flux coming out of the cube will be:-
Consider a coin of Example 1.20. It is electrically neutral and contains equal amounts of positive and negative charge of magnitude 34.8 kC. Suppose that these equal charges were concentrated in two point charges seperated by (i) 1 cm `(∼ 1/2 xx "diagonal of the one paisa coin")`, (ii) 100 m (~ length of a long 6 building) and (iii) 106 m (radius of the earth). Find the force on each such point charge in each of the three cases. What do you conclude from these results?
Figure represents a crystal unit of cesium chloride, CsCl. The cesium atoms, represented by open circles are situated at the corners of a cube of side 0.40 nm, whereas a Cl atom is situated at the centre of the cube.
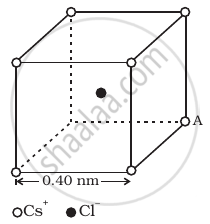
The Cs atoms are deficient in one electron while the Cl atom carries an excess electron.
- What is the net electric field on the Cl atom due to eight Cs atoms?
- Suppose that the Cs atom at the corner A is missing. What is the net force now on the Cl atom due to seven remaining Cs atoms?
