Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Figure represents a crystal unit of cesium chloride, CsCl. The cesium atoms, represented by open circles are situated at the corners of a cube of side 0.40 nm, whereas a Cl atom is situated at the centre of the cube.
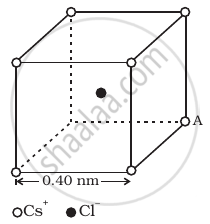
The Cs atoms are deficient in one electron while the Cl atom carries an excess electron.
- What is the net electric field on the Cl atom due to eight Cs atoms?
- Suppose that the Cs atom at the corner A is missing. What is the net force now on the Cl atom due to seven remaining Cs atoms?
उत्तर
- Zero, from symmetry.
- Removing a +ve Cs ion is equivalent to adding singly charged –ve Cs ion at that location.
Net force then is F = `e^2/(4pi ε_0 r^2)`
Where r = distance between the Cl ion and a Cs ion.
= `sqrt((0.20)^2 + (0.20)^2 + (0.20)^2) xx 10^-9` m
= `sqrt(3(0.20)^2) xx 10^-9` m
= 0.346 × 10–9 m
Hence, F = `((8.99 xx 10^9)(1.6 xx 10^-19)^2)/(0.346 xx 10^-9)^2` = 192 × 10–11
= 1.92 × 10–9 N, directed from A to Cl–
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the meaning of the statement ‘electric charge of a body is quantised’.
It is now believed that protons and neutrons (which constitute nuclei of ordinary matter) are themselves built out of more elementary units called quarks. A proton and a neutron consist of three quarks each. Two types of quarks, the so called ‘up’ quark (denoted by u) of charge (+2/3) e, and the ‘down’ quark (denoted by d) of charge (−1/3) e, together with electrons build up ordinary matter. (Quarks of other types have also been found which give rise to different unusual varieties of matter.) Suggest a possible quark composition of a proton and neutron.
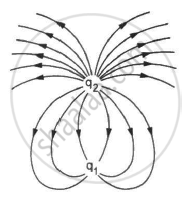
Consider the situation shown in the figure. What are the signs of q1 and q2? If the lines are drawn in proportion to the charges, what is the ratio q1/q2?
When a charged comb is brought near a small piece of paper, it attracts the piece. Does the paper become charged when the comb is brought near it?
In Figure 1 below, a charge Q is fixed. Another charge q is moved along a circular arc MN of radius r around it, from the point M to the point N such that the length of the arc MN = l. The work done in this process is:
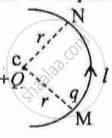
figure 1
A metallic sphere A isolated from ground is charged to +50 μC. This sphere is brought in contact with other isolated metallics sphere B of half the radius of sphere A. The charge on the two-sphere will be now in the ratio
Answer the following question.
State the law of conservation of charge.
Let x = πR`(("P"^2 - "Q"^2)/2)`, where P, Q and Rare lengths. The physical quantity x is ______.
A steady current of 8 mA flows through a wire. The number of electrons passing through a cross-section of the wire in 10 s is ______.
